A high-throughput screen targeting malaria transmission stages opens new avenues for drug development
- PMID: 21502082
- PMCID: PMC3080890
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir037
A high-throughput screen targeting malaria transmission stages opens new avenues for drug development
Abstract
A major goal of the worldwide malaria eradication program is the reduction and eventual elimination of malaria transmission. All currently available antimalarial compounds were discovered on the basis of their activity against the asexually reproducing red blood cell stages of the parasite, which are responsible for the morbidity and mortality of human malaria. Resistance against these compounds is widespread, and there is an urgent need for novel approaches to reduce the emergence of resistance to new antimalarials as they are introduced. We have established and validated the first high-throughput assay targeting the red blood cell parasite stage required for transmission, the sexually reproducing gametocyte. This assay will permit identification of compounds specifically targeting the transmission stages in addition to the asexual stage parasites. Such stage-specific compounds may be used in a combination therapy, reducing the emergence of resistance by blocking transmission of resistant parasites that may be selected in a patient.
Figures
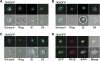
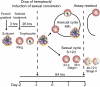
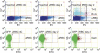


References
-
- Bruce MC, Alano P, Duthie S, Carter R. Commitment of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum to sexual and asexual development. Parasitology. 1990;100:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Healer J, McGuinness D, Carter R, Riley E. Transmission-blocking immunity to Plasmodium falciparum in malaria-immune individuals is associated with antibodies to the gamete surface protein Pfs230. Parasitology. 1999;119:425–33. - PubMed
-
- Butcher GA. Antimalarial drugs and the mosquito transmission of Plasmodium. Int J Parasitol. 1997;27:975–87. - PubMed
-
- Trager W, Jensen JB. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976;193:673–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

