Architecture of the mammalian Golgi
- PMID: 21502307
- PMCID: PMC3119909
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005181
Architecture of the mammalian Golgi
Abstract
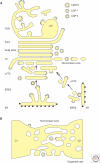
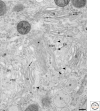
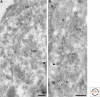
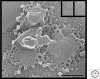
Since its first visualization in 1898, the Golgi has been a topic of intense morphological research. A typical mammalian Golgi consists of a pile of stapled cisternae, the Golgi stack, which is a key station for modification of newly synthesized proteins and lipids. Distinct stacks are interconnected by tubules to form the Golgi ribbon. At the entrance site of the Golgi, the cis-Golgi, vesicular tubular clusters (VTCs) form the intermediate between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stack. At the exit site of the Golgi, the trans-Golgi, the trans-Golgi network (TGN) is the major site of sorting proteins to distinct cellular locations. Golgi functioning can only be understood in light of its complex architecture, as was revealed by a range of distinct electron microscopy (EM) approaches. In this article, a general concept of mammalian Golgi architecture, including VTCs and the TGN, is described.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanoscale architecture of endoplasmic reticulum export sites and of Golgi membranes as determined by electron tomography.Plant Physiol. 2008 Aug;147(4):1454-68. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.120618. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18678738 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The plant Golgi apparatus--going with the flow.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jul 10;1744(3):466-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.06.006. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16038054 Review.
-
The plant Golgi apparatus--going with the flow.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jun 30;1744(2):93-107. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.03.009. Epub 2005 Apr 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. Corrected and republished in: Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jul 10;1744(3):466-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.06.006. PMID: 15922463 Corrected and republished. Review.
-
Golgi apparatus of epithelial principal cells of the epididymal initial segment of the rat: structure, relationship with endoplasmic reticulum, and role in the formation of secretory vesicles.Anat Rec. 1991 Feb;229(2):159-76. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092290203. Anat Rec. 1991. PMID: 1849381
-
Ultrastructural characterization of endoplasmic reticulum--Golgi transport containers (EGTC).J Cell Sci. 2002 Nov 15;115(Pt 22):4263-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00115. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12376558
Cited by
-
Accommodation of large cargo within Golgi cisternae.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;140(3):261-9. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1120-y. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23821163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular organization of the mammalian Golgi apparatus.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;24(4):467-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.05.009. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22726585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the human heparan sulfate polymerase complex EXT1-EXT2.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 19;13(1):7110. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34882-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36402845 Free PMC article.
-
A three-stage model of Golgi structure and function.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;140(3):239-49. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1128-3. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23881164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-step down-regulation of the secretory pathway in mitosis: a fresh perspective on protein trafficking.Bioessays. 2013 May;35(5):462-71. doi: 10.1002/bies.201200144. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 23494566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balch WE, McCaffery JM, Plutner H, Farquhar MG 1994. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is sorted and concentrated during export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 76: 841–852 - PubMed
-
- Bannykh SI, Nishimura N, Balch WE 1998. Getting into the Golgi. Trends Cell Biol 8: 21–25 - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C 2003. Signals for COPII-dependent export from the ER: what’s the ticket out?. Trends in cell biology 13: 295–300 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
