Regulation of Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata GABAergic Neuron Activity by H₂O₂ via Flufenamic Acid-Sensitive Channels and KATP Channels
- PMID: 21503158
- PMCID: PMC3074506
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2011.00014
Regulation of Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata GABAergic Neuron Activity by H₂O₂ via Flufenamic Acid-Sensitive Channels and KATP Channels
Abstract
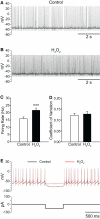
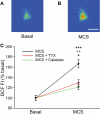
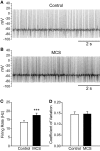
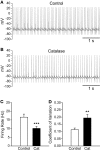
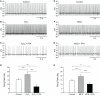
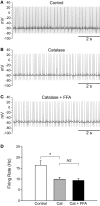
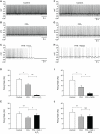
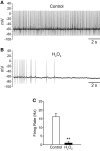
Substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) GABAergic neurons are key output neurons of the basal ganglia. Given the role of these neurons in motor control, it is important to understand factors that regulate their firing rate and pattern. One potential regulator is hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), a reactive oxygen species that is increasingly recognized as a neuromodulator. We used whole-cell current clamp recordings of SNr GABAergic neurons in guinea-pig midbrain slices to determine how H₂O₂ affects the activity of these neurons and to explore the classes of ion channels underlying those effects. Elevation of H₂O₂ levels caused an increase in the spontaneous firing rate of SNr GABAergic neurons, whether by application of exogenous H₂O₂ or amplification of endogenous H₂O₂ through inhibition of glutathione peroxidase with mercaptosuccinate. This effect was reversed by flufenamic acid (FFA), implicating transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. Conversely, depletion of endogenous H₂O₂ by catalase, a peroxidase enzyme, decreased spontaneous firing rate and firing precision of SNr neurons, demonstrating tonic control of firing rate by H₂O₂. Elevation of H₂O₂ in the presence of FFA revealed an inhibition of tonic firing that was prevented by blockade of ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channels with glibenclamide. In contrast to guinea-pig SNr neurons, the dominant effect of H₂O₂ elevation in mouse SNr GABAergic neurons was hyperpolarization, indicating a species difference in H₂O₂-dependent regulation. Thus, H₂O₂ is an endogenous modulator of SNr GABAergic neurons, acting primarily through presumed TRP channels in guinea-pig SNr, with additional modulation via K(ATP) channels to regulate SNr output.
Keywords: GABA; TRP channels; basal ganglia; diffusible messenger; hydrogen peroxide; reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRPM2 channels are required for NMDA-induced burst firing and contribute to H(2)O(2)-dependent modulation in substantia nigra pars reticulata GABAergic neurons.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;33(3):1157-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2832-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23325252 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism regulates the spontaneous firing of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons via KATP and nonselective cation channels.J Neurosci. 2014 Dec 3;34(49):16336-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1357-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25471572 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous hydrogen peroxide regulates the excitability of midbrain dopamine neurons via ATP-sensitive potassium channels.J Neurosci. 2005 Apr 27;25(17):4222-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4701-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15858048 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic and integrative properties of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons.Neuroscience. 2011 Dec 15;198:69-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.061. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21839148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABAergic control of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons.Prog Brain Res. 2007;160:189-208. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60011-3. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17499115 Review.
Cited by
-
Early dysfunction and progressive degeneration of the subthalamic nucleus in mouse models of Huntington's disease.Elife. 2016 Dec 20;5:e21616. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21616. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27995895 Free PMC article.
-
Flufenamic acid as an ion channel modulator.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 May;138(2):272-84. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.01.012. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23356979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical somatosensory-motor cortical response during vowel vocalization in spasmodic dysphonia.Clin Neurophysiol. 2019 Jun;130(6):1033-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30930193 Free PMC article.
-
H2O2: a dynamic neuromodulator.Neuroscientist. 2011 Aug;17(4):389-406. doi: 10.1177/1073858411404531. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Neuroscientist. 2011. PMID: 21666063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bursting activity of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons in mouse parkinsonism in awake and anesthetized states.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Mar;75:177-85. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.12.026. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25576395 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

