Reference values for respiratory system impedance using impulse oscillometry in healthy preschool children
- PMID: 21503199
- PMCID: PMC3077503
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2011.54.2.64
Reference values for respiratory system impedance using impulse oscillometry in healthy preschool children
Abstract
Purpose: The normal values for lung resistance and lung capacity of children, as determined by impulse oscillometry (IOS), are different for children of different ethnicities. However, reference values there is no available reference value for Korean preschool children have yet to be determined. The aim of the present study was to determine the normal ranges of IOS parameters in Korean preschool children.
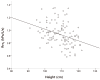
Methods: A total of 133 healthy Korean preschool children were selected from 639 children (aged 3 to 6 years) who attended kindergarten in Seongnam, Gyeonggi province, Korea. Healthy children were defined according to the European Respiratory Society (ERS) criteria. All subjects underwent lung function tests using IOS. The relationships between IOS value (respiratory resistance (Rrs) and reactance (Xrs) at 5 and 10 Hz and resonance frequency (RF)) and age, height, and weight were analyzed by simple linear and multiple linear regression analyses.
Results: The IOS success rate was 89.5%, yielding data on 119 children. Linear regression identified height as the best predictor of Rrs and Xrs. Using stepwise multiple linear regressions based on age, height, and weight, we determined regression equations and coefficients of determination (R(2)) for boys (Rrs(5)=1.934-0.009×Height, R(2)=12.1%; Xrs(5)=0.774+0.006×Height-0.002×Age, R(2)=20.2% and for girls (Rrs(5)=2.201-0.012×Height, R(2)=18.2%; Xrs(5)=-0.674+0.004×Height, R(2)=10.5%).
Conclusion: This study provides reference values for IOS measurements of normal Korean preschool children. These provide a basis for the diagnosis and monitoring of preschool children with a variety of respiratory diseases.
Keywords: Airway resistance; Impulse oscillation system; Preschool children; Reference values.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reference values of impulse oscillometry and its utility in the diagnosis of asthma in young Korean children.J Asthma. 2012 Oct;49(8):811-6. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2012.716472. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Asthma. 2012. PMID: 22953988
-
Reference values of impulse oscillometry (IOS) for healthy Chinese children aged 4-17 years.Respir Res. 2022 Jul 12;23(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02080-z. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35831898 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impulse oscillometry reference values and correlation with predictors in Turkish preschool children.Turk J Pediatr. 2019;61(4):560-567. doi: 10.24953/turkjped.2019.04.013. Turk J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31990474
-
Values of impulse oscillometry in healthy mexican children and adolescents.Respir Care. 2015 Jan;60(1):119-27. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03374. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Respir Care. 2015. PMID: 25336530
-
Forty years of reference values for respiratory system impedance in adults: 1977-2017.Respir Med. 2018 Mar;136:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29501245 Review.
Cited by
-
Impulse oscillometry reference values and bronchodilator response in three- to five-year old children living at high altitude.J Asthma Allergy. 2019 Sep 19;12:263-271. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S214297. eCollection 2019. J Asthma Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31571933 Free PMC article.
-
Interdevice agreement in respiratory resistance values by oscillometry in asthmatic children.ERJ Open Res. 2019 Mar 18;5(1):00138-2018. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00138-2018. eCollection 2019 Feb. ERJ Open Res. 2019. PMID: 30895187 Free PMC article.
-
Oscillometry reference values for children and adolescents.ERJ Open Res. 2024 Dec 16;10(6):00278-2024. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00278-2024. eCollection 2024 Nov. ERJ Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39698065 Free PMC article.
-
Is forced oscillation technique the next respiratory function test of choice in childhood asthma.World J Methodol. 2017 Dec 26;7(4):129-138. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.129. eCollection 2017 Dec 26. World J Methodol. 2017. PMID: 29354485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relating small airways to asthma control by using impulse oscillometry in children.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Mar;129(3):671-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Dec 17. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22178635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ip M, Karlberg J, Luk K, Leong J. Lung function reference values in Chinese children and adolescents in Hong Kong. I. Spirometric values and comparison with other populations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Beydon N, Lombardi E, Allen J, Arets H, Aurora P, Bisgaard H, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: pulmonary function testing in preschool children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:1304–1345. - PubMed
-
- Eigen H, Bieler H, Grant D, Christoph K, Terrill D, Heilman DK, et al. Spirometric pulmonary function in healthy preschool children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:619–623. - PubMed
-
- Kanengiser S, Dozor AJ. Forced expiratory maneuvers in children aged 3 to 5 years. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1994;18:144–149. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources