SON controls cell-cycle progression by coordinated regulation of RNA splicing
- PMID: 21504830
- PMCID: PMC3137374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.03.014
SON controls cell-cycle progression by coordinated regulation of RNA splicing
Abstract
It has been suspected that cell-cycle progression might be functionally coupled with RNA processing. However, little is known about the role of the precise splicing control in cell-cycle progression. Here, we report that SON, a large Ser/Arg (SR)-related protein, is a splicing cofactor contributing to efficient splicing of cell-cycle regulators. Downregulation of SON leads to severe impairment of spindle pole separation, microtubule dynamics, and genome integrity. These molecular defects result from inadequate RNA splicing of a specific set of cell-cycle-related genes that possess weak splice sites. Furthermore, we show that SON facilitates the interaction of SR proteins with RNA polymerase II and other key spliceosome components, suggesting its function in efficient cotranscriptional RNA processing. These results reveal a mechanism for controlling cell-cycle progression through SON-dependent constitutive splicing at suboptimal splice sites, with strong implications for its role in cancer and other human diseases.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
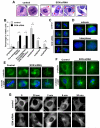
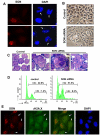

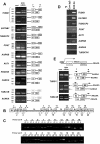
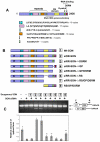

References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV. G-patch: a new conserved domain in eukaryotic RNA-processing proteins and type D retroviral polyproteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999;24:342–344. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL. Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of pre-mRNA processing factors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005;17:251–256. - PubMed
-
- Berdichevskii FB, Chumakov IM, Kiselev LL. Decoding of the primary structure of the son3 region in human genome: identification of a new protein with unusual structure and homology with DNA-binding proteins. Mol. Biol. (Mosk) 1988;22:794–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

