Crystallization and initial crystallographic analysis of AafA: the major adhesive subunit of the enteroaggregative Escherichia coli AAF/II pilus
- PMID: 21505239
- PMCID: PMC3080148
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111001412
Crystallization and initial crystallographic analysis of AafA: the major adhesive subunit of the enteroaggregative Escherichia coli AAF/II pilus
Abstract
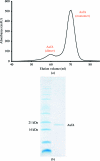
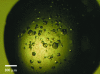
AafA is the major adhesive pilin subunit of the aggregative adherence fimbriae (AAF) from enteroaggregative Escherichia coli, which play an important role by attaching to the host cells during the initial phase of bacterial colonization and invasion. AafA has been crystallized at pH 3.4 and diffraction data have been collected to 2.1 Å resolution. Molecular replacement was unsuccessful and selenomethionine-substituted protein and heavy-atom derivatives are being prepared for phasing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural insight into host recognition by aggregative adherence fimbriae of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Sep 18;10(9):e1004404. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004404. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25232738 Free PMC article.
-
Complete 1H, 13C and 15N NMR assignments for donor-strand complemented AafA, the major pilin of aggregative adherence fimbriae (AAF/II) from enteroaggregative E. coli.Biomol NMR Assign. 2011 Apr;5(1):1-5. doi: 10.1007/s12104-010-9252-7. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Biomol NMR Assign. 2011. PMID: 20814767
-
Crystal structure and analysis of HdaB: The enteroaggregative Escherichia coli AAF/IV pilus tip protein.Protein Sci. 2016 Oct;25(10):1898-905. doi: 10.1002/pro.2982. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27400770 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of pap and type 1 fimbriation in Escherichia coli.Adv Microb Physiol. 2001;45:1-49. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(01)45001-6. Adv Microb Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11450107 Review.
-
Adhesins and invasins of pathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Oct;295(6-7):471-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.07.001. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16238021 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of cell surface-exposed proteins involved in the fimbria-mediated adherence of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli to intestinal cells.Infect Immun. 2014 Apr;82(4):1719-24. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01651-13. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24516112 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional studies of Escherichia coli aggregative adherence fimbriae (AAF/V) reveal a deficiency in extracellular matrix binding.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017 Mar;1865(3):304-311. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017. PMID: 27939608 Free PMC article.
-
Enteroaggregative E. coli Adherence to Human Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans Drives Segment and Host Specific Responses to Infection.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Sep 28;16(9):e1008851. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008851. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32986782 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into host recognition by aggregative adherence fimbriae of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Sep 18;10(9):e1004404. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004404. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25232738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, K. L. et al. (2004). Mol. Cell, 15, 647–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

