Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of ThiM from Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 21505246
- PMCID: PMC3080155
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111004192
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of ThiM from Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
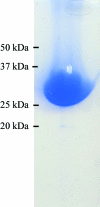
ThiM [5-(hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazole kinase; EC 2.7.1.50] from Staphylococcus aureus is an essential enzyme of thiamine or vitamin B(1) metabolism and has been crystallized by the vapour-diffusion method. The crystals belonged to the primitive space group P1, with unit-cell parameters a = 62.06, b = 62.40, c = 107.82 Å, α = 92.25, β = 91.37, γ = 101.48° and six protomers in the unit cell, corresponding to a packing parameter V(M) of 2.3 Å(3) Da(-1). Diffraction data were collected to 2.1 Å resolution using synchrotron radiation. The phase problem was solved by molecular replacement.
Figures

References
-
- Apodaca, A. A. & Rakita, R. M. (2003). N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 86–87. - PubMed
-
- Begley, T. P., Downs, D. M., Ealick, S. E., McLafferty, F. W., Van Loon, A. P., Taylor, S., Campobasso, N., Chiu, H.-J., Kinsland, C., Reddick, J. J. & Xi, J. (1999). Arch. Microbiol. 171, 293–300. - PubMed
-
- Campobasso, N., Mathews, I. I., Begley, T. P. & Ealick, S. E. (2000). Biochemistry, 39, 7868–7877. - PubMed
-
- Klevens, R. M. et al. (2007). JAMA, 298, 1763–1771. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

