Not(ch) just development: Notch signalling in the adult brain
- PMID: 21505516
- PMCID: PMC3159580
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3024
Not(ch) just development: Notch signalling in the adult brain
Abstract
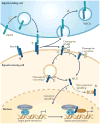
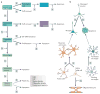
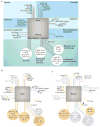
The Notch pathway is often regarded as a developmental pathway, but components of Notch signalling are expressed and active in the adult brain. With the advent of more sophisticated genetic manipulations, evidence has emerged that suggests both conserved and novel roles for Notch signalling in the adult brain. Not surprisingly, Notch is a key regulator of adult neural stem cells, but it is increasingly clear that Notch signalling also has roles in the regulation of migration, morphology, synaptic plasticity and survival of immature and mature neurons. Understanding the many functions of Notch signalling in the adult brain, and its dysfunction in neurodegenerative disease and malignancy, is crucial to the development of new therapeutics that are centred around this pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Louvi A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Notch signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nature Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Yoon K, Gaiano N. Notch signaling in the mammalian central nervous system: insights from mouse mutants. Nature Neurosci. 2005;8:709–715. - PubMed
-
- Berezovska O, Xia MQ, Hyman BT. Notch is expressed in adult brain, is coexpressed with presenilin-1, and is altered in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998;57:738–745. - PubMed
-
- Sestan N, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rakic P. Contact-dependent inhibition of cortical neurite growth mediated by notch signaling. Science. 1999;286:741–746. This paper is the first to show Notch function in postmitotic neurons in regulating density-dependent dendritic arborization. - PubMed
-
- Li L, et al. Alagille syndrome is caused by mutations in human Jagged1, which encodes a ligand for Notch1. Nature Genet. 1997;16:243–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

