Microdialysis combined with proteomics for protein identification in breast tumor microenvironment in vivo
- PMID: 21505562
- PMCID: PMC3047629
- DOI: 10.1007/s12307-010-0046-3
Microdialysis combined with proteomics for protein identification in breast tumor microenvironment in vivo
Abstract
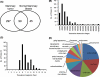
Tumor microenvironment constitutes a reservoir for proteins released from tumor cells and the host, which can contribute significantly to tumor growth and invasion. This study aims to apply a method of combining in vivo microdialysis and proteomics to identify proteins in mammary tumor interstitial fluids, a major component of tumor microenvironment. In vivo microdialysis was performed in polyomavirus middle T antigen (PyVmT) transgenic mouse mammary tumors and age-matched control wild-type mammary glands. Over four hundred proteins were identified from the microdialysis perfusates, using the Multidimensional Protein Identification Technology. Osteopontin (OPN) is one of the proteins overexpressed in breast tumor perfusates, as confirmed with immunoassays. OPN was also found to be present in tumor-associated stroma in both PyVmT and human breast tumors, using immunohistochemistry. Specifically, fibroblasts were further shown to express OPN at both mRNA and protein levels. In vitro assays showed that OPN can stimulate PyVmT breast carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Finally, the expression of OPN was significantly higher in the peripheral blood of mice bearing breast tumors, compared to wild-type mice. Overall, microdialysis combined with proteomics is a unique technique for identifying proteins in a tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mammary fibroblasts can secrete OPN, and its overexpression in mammary tumor microenvironment may contribute significantly to mammary tumor progression.
Electronic supplementary material: The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s12307-010-0046-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Fibroblasts; Microdialysis; Osteopontin; Proteomics; Tumor microenvironment.
Figures

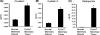

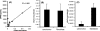

Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of metastasis in a polyomavirus middle T mouse model: the role of osteopontin.Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6(3):R157-69. doi: 10.1186/bcr768. Epub 2004 Feb 25. Breast Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15084239 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of promoter regions involved in cell- and developmental stage-specific osteopontin expression in bone, kidney, placenta, and mammary gland: an analysis of transgenic mice.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Jan;19(1):78-88. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2004.19.1.78. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 14753740
-
Loss of host-derived osteopontin creates a glioblastoma-promoting microenvironment.Neuro Oncol. 2018 Feb 19;20(3):355-366. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox165. Neuro Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29016864 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin as a therapeutic target for cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Aug;18(8):883-95. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.925447. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 24899149 Review.
-
Role of the metastasis-promoting protein osteopontin in the tumour microenvironment.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Aug;14(8):2037-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01115.x. Epub 2010 Jul 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20597997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Angiogenic Secretome in VEGF overexpressing Breast Cancer Xenografts.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 20;6:39460. doi: 10.1038/srep39460. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27995973 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts secreting osteopontin promote growth of luminal breast cancer.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Jun 11;27(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00351-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35690734 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the proteomic investigation of the cell secretome.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2012 Jun;9(3):337-45. doi: 10.1586/epr.12.21. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22809211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Interstitial Fluid Formation, Characterization, and Clinical Implications.Front Oncol. 2015 May 26;5:115. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00115. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26075182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo microdialysis sampling of adipokines CCL2, IL-6, and leptin in the mammary fat pad of adult female rats.Mol Biosyst. 2014 Apr;10(4):806-12. doi: 10.1039/c3mb70308h. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Mol Biosyst. 2014. PMID: 24457312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ronnov-Jessen L, Petersen OW, Bissell MJ. Physiol Rev. 1996;76:69–125. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
