Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: role of paracrine soluble factors
- PMID: 21506195
- PMCID: PMC3293251
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.643
Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: role of paracrine soluble factors
Abstract
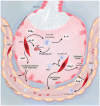
Morbidity and mortality have declined only modestly in patients with clinical acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), despite extensive research into the pathophysiology. Current treatment remains primarily supportive with lung-protective ventilation and a fluid conservative strategy. Pharmacologic therapies that reduce the severity of lung injury in preclinical models have not yet been translated to effective clinical treatment options. Consequently, further research in translational therapies is needed. Cell-based therapy with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is one attractive new therapeutic approach. MSCs have the capacity to secrete multiple paracrine factors that can regulate endothelial and epithelial permeability, decrease inflammation, enhance tissue repair, and inhibit bacterial growth. This review will focus on recent studies, which support the potential therapeutic use of MSCs in ALI/ARDS, with an emphasis on the role of paracrine soluble factors.
Copyright © 2011 AlphaMed Press.
Figures
References
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6:230–247. - PubMed
-
- Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8:315–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

