HC-Pro silencing suppressor significantly alters the gene expression profile in tobacco leaves and flowers
- PMID: 21507209
- PMCID: PMC3111369
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-68
HC-Pro silencing suppressor significantly alters the gene expression profile in tobacco leaves and flowers
Abstract
Background: RNA silencing is used in plants as a major defence mechanism against invasive nucleic acids, such as viruses. Accordingly, plant viruses have evolved to produce counter defensive RNA-silencing suppressors (RSSs). These factors interfere in various ways with the RNA silencing machinery in cells, and thereby disturb the microRNA (miRNA) mediated endogene regulation and induce developmental and morphological changes in plants. In this study we have explored these effects using previously characterized transgenic tobacco plants which constitutively express (under CaMV 35S promoter) the helper component-proteinase (HC-Pro) derived from a potyviral genome. The transcript levels of leaves and flowers of these plants were analysed using microarray techniques (Tobacco 4 × 44 k, Agilent).
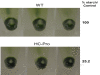
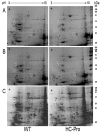
Results: Over expression of HC-Pro RSS induced clear phenotypic changes both in growth rate and in leaf and flower morphology of the tobacco plants. The expression of 748 and 332 genes was significantly changed in the leaves and flowers, respectively, in the HC-Pro expressing transgenic plants. Interestingly, these transcriptome alterations in the HC-Pro expressing tobacco plants were similar as those previously detected in plants infected with ssRNA-viruses. Particularly, many defense-related and hormone-responsive genes (e.g. ethylene responsive transcription factor 1, ERF1) were differentially regulated in these plants. Also the expression of several stress-related genes, and genes related to cell wall modifications, protein processing, transcriptional regulation and photosynthesis were strongly altered. Moreover, genes regulating circadian cycle and flowering time were significantly altered, which may have induced a late flowering phenotype in HC-Pro expressing plants. The results also suggest that photosynthetic oxygen evolution, sugar metabolism and energy levels were significantly changed in these transgenic plants. Transcript levels of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) were also decreased in these plants, apparently leading to decreased transmethylation capacity. The proteome analysis using 2D-PAGE indicated significantly altered proteome profile, which may have been both due to altered transcript levels, decreased translation, and increased proteosomal/protease activity.
Conclusion: Expression of the HC-Pro RSS mimics transcriptional changes previously shown to occur in plants infected with intact viruses (e.g. Tobacco etch virus, TEV). The results indicate that the HC-Pro RSS contributes a significant part of virus-plant interactions by changing the levels of multiple cellular RNAs and proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of geminiviral AC2 RNA silencing suppressor changes sugar and jasmonate responsive gene expression in transgenic tobacco plants.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Nov 7;12:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-204. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23130567 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylic acid-mediated and RNA-silencing defense mechanisms cooperate in the restriction of systemic spread of plum pox virus in tobacco.Plant J. 2006 Oct;48(2):217-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02861.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 17018032
-
Discriminating mutations of HC-Pro of zucchini yellow mosaic virus with differential effects on small RNA pathways involved in viral pathogenicity and symptom development.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2010 Jan;23(1):17-28. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-23-1-0017. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2010. PMID: 19958135
-
Overexpression of PsnSuSy1, 2 genes enhances secondary cell wall thickening, vegetative growth, and mechanical strength in transgenic tobacco.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;100(3):215-230. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00850-w. Epub 2019 May 4. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. Retraction in: Plant Mol Biol. 2023 May;112(1-2):105. doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01353-5. PMID: 31053988 Retracted. Review.
-
Viral RNA silencing suppressors (RSS): novel strategy of viruses to ablate the host RNA interference (RNAi) defense system.Virus Res. 2011 Jan;155(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.10.003. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20951748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppress to Survive-Implication of Plant Viruses in PTGS.Plant Mol Biol Report. 2015;33(3):335-346. doi: 10.1007/s11105-014-0755-8. Plant Mol Biol Report. 2015. PMID: 25999662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimation of the functions of viral RNA silencing suppressors by apple latent spherical virus vector.Virus Genes. 2020 Feb;56(1):67-77. doi: 10.1007/s11262-019-01708-5. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Virus Genes. 2020. PMID: 31646461
-
Expression of geminiviral AC2 RNA silencing suppressor changes sugar and jasmonate responsive gene expression in transgenic tobacco plants.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Nov 7;12:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-204. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23130567 Free PMC article.
-
Plant viral proteins and fibrillarin: the link to complete the infective cycle.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 May;48(5):4677-4686. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06401-1. Epub 2021 May 25. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34036480 Review.
-
Citrus tristeza virus-host interactions.Front Microbiol. 2013 May 14;4:88. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00088. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23717303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wadsworth S, Dunoyer P. In: Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. Bouarab, editor. Anonymous CAB international; 2009. Plant RNA-silencing immunity and viral counter-defence strategies; pp. 1–35. pp.1-35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

