Genetic influences of cortical gray matter in language-related regions in healthy controls and schizophrenia
- PMID: 21507613
- PMCID: PMC3110636
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2011.03.027
Genetic influences of cortical gray matter in language-related regions in healthy controls and schizophrenia
Abstract
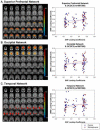
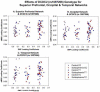
Individuals with schizophrenia show a broad range of language impairments, including reading difficulties. A recent structural MRI (sMRI) study linked these difficulties to structural abnormalities in language-related regions (Leonard et al., 2008). Similar regions have been implicated in primary reading disability (RD). Major hypotheses of RD implicate abnormal embryonic neuronal migration in the cortex, and genetic linkage and association studies have identified a number of candidate RD genes that are associated with neuronal migration (Paracchini et al., 2007). Interestingly, evidence suggests at least some individuals with schizophrenia also show impaired neuronal migration in the cortex (Akbarian et al., 1996). Thus the aim of this study was to examine the link between RD-related genes and gray matter volumes in healthy controls and schizophrenia. We used parallel independent component analysis (parallel-ICA) to examine the relationship between gray matter volumes extracted using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and 16 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) spanning FOXP2 and four RD-related genes, DCDC2, DYX1C1, KIAA0319 and TTRAP. Parallel-ICA identified five sMRI-SNP relationships. Superior and inferior cerebellar networks were related to DYX1C1 and DCDC2/KIAA0319 respectively in both groups. The superior prefrontal, temporal and occipital networks were positively related to DCDC2 in the schizophrenia, but not the control group. The identified networks closely correspond to the known distribution of language processes in the cortex. Thus, reading and language difficulties in schizophrenia may be related to distributed cortical structural abnormalities associated with RD-related genes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic influences of resting state fMRI activity in language-related brain regions in healthy controls and schizophrenia patients: a pilot study.Brain Imaging Behav. 2013 Mar;7(1):15-27. doi: 10.1007/s11682-012-9168-1. Brain Imaging Behav. 2013. PMID: 22669497 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants of FOXP2 and KIAA0319/TTRAP/THEM2 locus are associated with altered brain activation in distinct language-related regions.J Neurosci. 2012 Jan 18;32(3):817-25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5996-10.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22262880 Free PMC article.
-
DISC1 (disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1) is associated with cortical grey matter volumes in the human brain: a voxel-based morphometry (VBM) study.J Psychiatr Res. 2013 Feb;47(2):188-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Nov 8. J Psychiatr Res. 2013. PMID: 23140672
-
Progress towards a cellular neurobiology of reading disability.Neurobiol Dis. 2010 May;38(2):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.06.019. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Neurobiol Dis. 2010. PMID: 19616627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional deficits in brain volume in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies.Am J Psychiatry. 2005 Dec;162(12):2233-45. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.12.2233. Am J Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16330585 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction effect between handedness and CNTNAP2 polymorphism (rs7794745 genotype) on voice-specific frontotemporal activity in healthy individuals: an fMRI study.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Apr 20;9:87. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00087. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25941478 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenetics of developmental dyslexia: from genes to behavior through brain neuroimaging and cognitive and sensorial mechanisms.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 3;7(1):e987. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.240. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28045463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of Kiaa0319 knockdown on cortical and subcortical anatomy in male rats.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Apr;31(2):116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.11.008. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23220223 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic influences of resting state fMRI activity in language-related brain regions in healthy controls and schizophrenia patients: a pilot study.Brain Imaging Behav. 2013 Mar;7(1):15-27. doi: 10.1007/s11682-012-9168-1. Brain Imaging Behav. 2013. PMID: 22669497 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Schizophrenia Detection Using Multimodality Media via a Text Reading Task.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 14;16:933049. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.933049. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35911987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hetrick WP, Bunney WE, Jr, Jone EG. Maldistribution of interstitial neurons in prefrontal white matter of the brains of schizophrenia patients. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1996;53:425–436. - PubMed
-
- Allen P, Laroi F, McGuire PK, Aleman A. The hallucinating brain: a review of structural and functional neuroimaging studies of hallucinations. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2008;32:175–191. - PubMed
-
- Brambati SM, Termine C, Ruffino M, Stella G, Fazio F, Cappa SF, et al. Regional reductions of gray matter volume in familial dyslexia. Neurology. 2004;63:742–745. - PubMed
-
- Brown W, Eliez S, Menon V, Rumsey J, White C, Reiss A. Preliminary evidence of widespread morphological variations in the brain in dyslexia. Neurology. 2001;56:781–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

