RNA elements directing translation of the duck hepatitis B Virus polymerase via ribosomal shunting
- PMID: 21507974
- PMCID: PMC3126499
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00101-11
RNA elements directing translation of the duck hepatitis B Virus polymerase via ribosomal shunting
Abstract
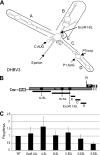
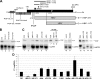
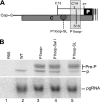
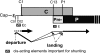
The duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) reverse transcriptase (P) is translated from the downstream position on a bicistronic mRNA, called the pregenomic RNA, through a poorly characterized ribosomal shunt. Here, the positions of the discontinuous ribosomal transfer during shunting were mapped, and RNA elements important for shunting were identified as a prelude to dissecting the shunting mechanism. Mutations were introduced into the DHBV genome, genomic expression vectors were transfected into cells which support reverse transcription, and P translation efficiency was defined as the ratio of P/mRNA. Five observations were made. First, ribosomes departed from sequences that comprise the RNA stem-loop called ε that is key to viral replication, but the known elements of ε were not needed for shunting. Second, at least two landing sites for ribosomes were found on the mRNA. Third, all sequences upstream of ε, most sequences between the cap and the P AUG, and sequences within the P-coding region were dispensable for shunting. Fourth, elements on the mRNA involved in reverse transcription or predicted to be involved in shunting on the basis of mechanisms documented in other viruses, including short open reading frames near the departure site, were not essential for shunting. Finally, two RNA elements in the 5' portion of the mRNA were found to assist shunting. These observations are most consistent with shunting being directed by signals that act through an uncharacterized RNA secondary structure. Together, these data indicate that DHBV employs either a novel shunting mechanism or a major variation on one of the characterized mechanisms.
Figures



References
-
- Chang C., Hirsch R. C., Ganem D. 1995. Sequences in the preC region of duck hepatitis B virus affect pregenomic RNA accumulation. Virology 207:549–554 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

