Inhibition of dengue virus through suppression of host pyrimidine biosynthesis
- PMID: 21507975
- PMCID: PMC3126545
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02510-10
Inhibition of dengue virus through suppression of host pyrimidine biosynthesis
Abstract
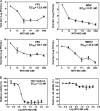
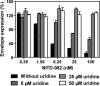
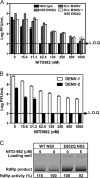
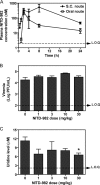
Viral replication relies on the host to supply nucleosides. Host enzymes involved in nucleoside biosynthesis are potential targets for antiviral development. Ribavirin (a known antiviral drug) is such an inhibitor that suppresses guanine biosynthesis; depletion of the intracellular GTP pool was shown to be the major mechanism to inhibit flavivirus. Along similar lines, inhibitors of the pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway could be targeted for potential antiviral development. Here we report on a novel antiviral compound (NITD-982) that inhibits host dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), an enzyme required for pyrimidine biosynthesis. The inhibitor was identified through screening 1.8 million compounds using a dengue virus (DENV) infection assay. The compound contains an isoxazole-pyrazole core structure, and it inhibited DENV with a 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) of 2.4 nM and a 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC(50)) of >5 μM. NITD-982 has a broad antiviral spectrum, inhibiting both flaviviruses and nonflaviviruses with nanomolar EC(90)s. We also show that (i) the compound inhibited the enzymatic activity of recombinant DHODH, (ii) an NITD-982 analogue directly bound to the DHODH protein, (iii) supplementing the culture medium with uridine reversed the compound-mediated antiviral activity, and (iv) DENV type 2 (DENV-2) variants resistant to brequinar (a known DHODH inhibitor) were cross resistant to NITD-982. Collectively, the results demonstrate that the compound inhibits DENV through depleting the intracellular pyrimidine pool. In contrast to the in vitro potency, the compound did not show any efficacy in the DENV-AG129 mouse model. The lack of in vivo efficacy is likely due to the exogenous uptake of pyrimidine from the diet or to a high plasma protein-binding activity of the current compound.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel AR-12 derivatives, P12-23 and P12-34, inhibit flavivirus replication by blocking host de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018 Nov 21;7(1):187. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0191-1. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018. PMID: 30459406 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of dengue virus by an ester prodrug of an adenosine analog.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Aug;54(8):3255-61. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00397-10. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20516277 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of dengue virus resistance to brequinar in cell culture.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Sep;54(9):3686-95. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00561-10. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20606073 Free PMC article.
-
Ten years of dengue drug discovery: progress and prospects.Antiviral Res. 2013 Nov;100(2):500-19. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 24076358 Review.
-
[Stimulation of the antiviral innate immune response by pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors: a surprise of phenotypic screening].Med Sci (Paris). 2015 Jan;31(1):98-104. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20153101019. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Med Sci (Paris). 2015. PMID: 25658737 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Novel and potent inhibitors targeting DHODH are broad-spectrum antivirals against RNA viruses including newly-emerged coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.Protein Cell. 2020 Oct;11(10):723-739. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00768-w. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Protein Cell. 2020. PMID: 32754890 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted LC-MS metabolomic studies of Asteraceae species to discover inhibitors of Leishmania major dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.Metabolomics. 2019 Apr 4;15(4):59. doi: 10.1007/s11306-019-1520-7. Metabolomics. 2019. PMID: 30949823
-
Identification and Characterization of Novel Compounds with Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity against Influenza A and B Viruses.J Virol. 2020 Mar 17;94(7):e02149-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02149-19. Print 2020 Mar 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31941776 Free PMC article.
-
Cross Talk between Nucleotide Synthesis Pathways with Cellular Immunity in Constraining Hepatitis E Virus Replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Apr 22;60(5):2834-48. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02700-15. Print 2016 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26926637 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Compound That Inhibits Pyrimidine Biosynthesis and Establishes a Type 1 Interferon-Independent Antiviral State.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):4552-62. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00282-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27185801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackermann M., Padmanabhan R. 2001. De novo synthesis of RNA by the dengue virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase exhibits temperature dependence at the initiation but not elongation phase. J. Biol. Chem. 276:39926–39937 - PubMed
-
- Bader B., Knecht W., Fries M., Loffler M. 1998. Expression, purification, and characterization of histidine-tagged rat and human flavoenzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Protein Expr. Purif 13:414–422 - PubMed
-
- Bartelma G., Padmanabhan R. 2002. Expression, purification, and characterization of the RNA 5′-triphosphatase activity of dengue virus type 2 nonstructural protein 3. Virology 299:122–132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

