Detoxification: a novel function of BRCA1 in tumor suppression?
- PMID: 21507987
- PMCID: PMC3143468
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr089
Detoxification: a novel function of BRCA1 in tumor suppression?
Abstract
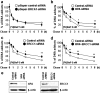
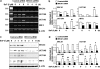
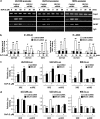
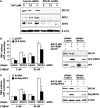
Our studies found that BRCA1 levels negatively correlate with DNA adducts induced by Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP). Pulse-chase experiments showed that the increase in BaP-induced DNA adducts in BRCA1 knockdown cells may not be associated with BRCA1's function in nucleotide excision repair activity; rather, it may be associated with its function in modulating transcriptional regulation. BRCA1 knockdown in MCF-10A cells significantly attenuated the induction of CYP1A1 following BaP treatment indicating that the increase in BaP-induced adducts in BRCA1 knockdown cells is not CYP1A1 dependent. However, our study shows that BRCA1 defective cells may still be able to biotransform BaP by regulating other CYP enzymes, including CYP1B1. Knockdown of BRCA1 also severely affected the expression levels of two types of uridine diphosphate glucorunyltransferase (UGT1A1 and UGT1A9) and NRF2. Both UGTs are known as BaP-specific detoxification enzymes, and NRF2 is a master regulator of antioxidant and detoxification genes. Thus, we concluded that the increased amount of BaP-induced DNA adducts in BRCA1 knockdown cells is strongly associated with its loss of functional detoxification. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay revealed that BRCA1 is recruited to the promoter/enhancer sequences of UGT1A1, UGT1A9, and NRF2. Regulation of UGT1A1 and UGT1A9 expression showed that the induction of DNA adducts by BaP is directly affected by their expression levels. Finally, overexpression of UGTs, NRF2, or ARNT significantly decreased the amount of BaP-induced adducts in BRCA1-deficient cells. Overall, our results suggest that BRCA1 protects cells by reducing the amount of BaP-induced DNA adducts possibly via transcriptional activation of detoxification gene expression.
Figures




References
-
- Abbott DW, Thompson ME, Robinson-Benion C, Tomlinson G, Jensen RA, Holt JT. BRCA1 expression restores radiation resistance in BRCA1-defective cancer cells through enhancement of transcription-coupled DNA repair. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:18808–18812. - PubMed
-
- Ali AB, Iau PT, Sng JH. Cancer-specific methylation in the BRCA1 promoter in sporadic breast tumours. Med. Oncol. 2011;28:64–66. - PubMed
-
- Bae I, Fan S, Meng Q, Rih JK, Kim HJ, Kang HJ, Xu J, Goldberg ID, Jaiswal AK, Rosen EM. BRCA1 induces antioxidant gene expression and resistance to oxidative stress. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7893–7909. - PubMed
-
- Bochar DA, Wang L, Beniya H, Kinev A, Xue Y, Lane WS, Wang W, Kashanchi F, Shiekhattar R. BRCA1 is associated with a human SWI/SNF-related complex: linking chromatin remodeling to breast cancer. Cell. 2000;102:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Breast Cancer Family Registry, Kathleen Cuningham Consortium for Research into Familial Breast Cancer (Australasia), Ontario Cancer Genetics Network (Canada) Smoking and risk of breast cancer in carriers of mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 aged less than 50 years. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008;109:67–75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

