Aflatoxin B1-DNA adduct formation and mutagenicity in livers of neonatal male and female B6C3F1 mice
- PMID: 21507988
- PMCID: PMC3143467
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr087
Aflatoxin B1-DNA adduct formation and mutagenicity in livers of neonatal male and female B6C3F1 mice
Erratum in
- Toxicol Sci. 2012 Jan;125(1):326. Bouhenguel, Jason T [added]
Abstract
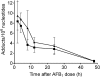
Exposure to genotoxic chemicals at a young age increases cancer incidence later in life. Aflatoxin B(1) (AFB(1)) is a potent genotoxin that induces hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in many animal species and in humans. Whereas adult mice are insensitive to aflatoxin-induced carcinogenesis, mice treated with AFB(1) shortly after birth develop a high incidence of HCC in adulthood. Furthermore, the incidence of HCC in adult male mice treated as infants is much greater than in females, reasons for which are unclear. In this study, treatment with AFB(1) produced similar levels of DNA damage and mutations in the liver of newborn male and female gpt delta B6C3F1 mice. Twenty-four hours after dosing with AFB(1) (6 mg/kg), the highly mutagenic AFB(1)-FAPY adduct was present at twice the level of AFB(1)-N(7)-guanine in liver DNA of males and females. A multiple dose regimen (3 × 2 mg/kg), while delivering the same total dose, resulted in lower AFB(1) adduct levels. Mutation frequencies in the gpt transgene in liver were increased by 20- to 30-fold. The most prominent mutations in AFB(1)-treated mice were G:C to T:A transversions and G:C to A:T transitions. At this 21-day time point, no significant differences were found in mutation frequency or types of mutations between males and females. These results show that infant male and female B6C3F1 mice experience similar amounts of DNA damage and mutation from AFB(1) that may initiate the neoplastic process. The gender difference in the subsequent development of HCC highlights the importance of elucidating additional factors that modulate HCC development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro recapitulating of TP53 mutagenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with dietary aflatoxin B1 exposure.Gastroenterology. 2009 Sep;137(3):1127-37, 1137.e1-5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19524575 Free PMC article.
-
The aflatoxin B(1) formamidopyrimidine adduct plays a major role in causing the types of mutations observed in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 May 14;99(10):6655-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.102167699. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12011430 Free PMC article.
-
Bypass of aflatoxin B1 adducts by the Sulfolobus solfataricus DNA polymerase IV.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Aug 17;133(32):12556-68. doi: 10.1021/ja2015668. Epub 2011 Jul 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21790157 Free PMC article.
-
The chemistry and biology of aflatoxin B(1): from mutational spectrometry to carcinogenesis.Carcinogenesis. 2001 Apr;22(4):535-45. doi: 10.1093/carcin/22.4.535. Carcinogenesis. 2001. PMID: 11285186 Review.
-
Dietary modulation of the biotransformation and genotoxicity of aflatoxin B(1).Toxicology. 2012 Sep 28;299(2-3):69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.05.016. Epub 2012 May 26. Toxicology. 2012. PMID: 22640941 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of DNA lesion repair, replication and formation on the mutational spectra of environmental carcinogens: Aflatoxin B1 as a case study.DNA Repair (Amst). 2018 Nov;71:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Aug 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30309820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Polymer Nanoformulations in Hepatoma Therapy by Established Rodent Models.Theranostics. 2019 Feb 20;9(5):1426-1452. doi: 10.7150/thno.31683. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 30867842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced 4-aminobiphenyl-induced liver tumorigenicity but not DNA damage in arylamine N-acetyltransferase null mice.Cancer Lett. 2012 May 28;318(2):206-13. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.022. Epub 2011 Dec 19. Cancer Lett. 2012. PMID: 22193722 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational spectra of aflatoxin B1 in vivo establish biomarkers of exposure for human hepatocellular carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Apr 11;114(15):E3101-E3109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700759114. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28351974 Free PMC article.
-
Context Matters: Contribution of Specific DNA Adducts to the Genotoxic Properties of the Tobacco-Specific Nitrosamine NNK.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Jan 17;30(1):420-433. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00386. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28092943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams WT, Skopek TR. Statistical test for the comparison of samples from mutational spectra. J. Mol. Biol. 1987;194:391–396. - PubMed
-
- Benasutti M, Ejadi S, Whitlow MD, Loechler EL. Mapping the binding site of aflatoxin B1 in DNA: systematic analysis of the reactivity of aflatoxin B1 with guanines in different DNA sequences. Biochemistry. 1988;27:472–481. - PubMed
-
- Brown KL, Deng JZ, Iyer RS, Iyer LG, Voehler MW, Stone MP, Harris CM, Harris TM. Unraveling the aflatoxin-FAPY conundrum: structural basis for differential replicative processing of isomeric forms of the formamidopyrimidine-type DNA adduct of aflatoxin B1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:15188–15199. - PMC - PubMed

