Volumetric imaging of fish locomotion
- PMID: 21508026
- PMCID: PMC3169073
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2011.0282
Volumetric imaging of fish locomotion
Abstract
Fishes use multiple flexible fins in order to move and maintain stability in a complex fluid environment. We used a new approach, a volumetric velocimetry imaging system, to provide the first instantaneous three-dimensional views of wake structures as they are produced by freely swimming fishes. This new technology allowed us to demonstrate conclusively the linked ring vortex wake pattern that is produced by the symmetrical (homocercal) tail of fishes, and to visualize for the first time the three-dimensional vortex wake interaction between the dorsal and anal fins and the tail. We found that the dorsal and anal fin wakes were rapidly (within one tail beat) assimilated into the caudal fin vortex wake. These results show that volumetric imaging of biologically generated flow patterns can reveal new features of locomotor dynamics, and provides an avenue for future investigations of the diversity of fish swimming patterns and their hydrodynamic consequences.
Figures
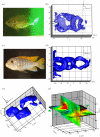
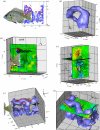
References
-
- Alben S., Madden P. G. A., Lauder G. V. 2007. The mechanics of active fin-shape control in ray-finned fishes. J. R. Soc. Interface 4, 243–25610.1098/rsif.2006.0181 (doi:10.1098/rsif.2006.0181) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge R. 1963. Caudal fin and body movement in the propulsion of some fish. J. Exp. Biol. 40, 23–56
-
- Drucker E. G., Lauder G. V. 2005. Locomotor function of the dorsal fin in rainbow trout: kinematic patterns and hydrodynamic forces. J. Exp. Biol. 208, 4479–449410.1242/jeb.01922 (doi:10.1242/jeb.01922) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Flammang B. E., Lauder G. V. 2008. Speed-dependent intrinsic caudal fin muscle recruitment during steady swimming in bluegill sunfish, Lepomis macrochirus. J. Exp. Biol. 211, 587–59810.1242/jeb.012096 (doi:10.1242/jeb.012096) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jayne B. C., Lozada A. F., Lauder G. V. 1996. Function of the dorsal fin in bluegill sunfish: motor patterns during four distinct locomotor behaviors. J. Morphol. 228, 307–32610.1002/(SICI)1097-4687(199606)228:3<307::AID-JMOR3>3.0.CO;2-Z (doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4687(199606)228:3<307::AID-JMOR3>3.0.CO;2-Z) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

