Comparison of two multiplex methods for detection of respiratory viruses: FilmArray RP and xTAG RVP
- PMID: 21508156
- PMCID: PMC3147849
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02582-10
Comparison of two multiplex methods for detection of respiratory viruses: FilmArray RP and xTAG RVP
Abstract
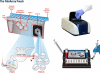
We compared the FilmArray RP (Idaho Technology, Inc., Salt Lake City, UT) and the xTAG RVP (Luminex Corporation, Toronto, Canada) multiplex respiratory virus PCR methods for the detection of respiratory viruses in a set of 200 patient specimens frozen at -70 °C after standard viral culture and antigen detection methods were done. Both systems detected between 40 to 50% more viruses than traditional methods, primarily rhinoviruses and human metapneumovirus. The FilmArray RP detected significantly more total viruses either alone or as part of mixed infections than the xTAG RVP, as well as an additional 21.6% more respiratory syncytial viruses. The xTAG RVP requires 5 to 6 h with 2.5 to 3 h of hands-on time, while the FilmArray RP takes about an hour with 3 to 5 min of hands-on time, making it much easier to perform.
Figures

References
-
- Gerna G., et al. 2008. Correlation of viral load as determined by real-time RT-PCR and clinical characteristics of respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infections in early infancy. J. Clin. Virol. 41:45–48 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

