Kinetics and magnitude of antibody responses against the conserved 47-kilodalton antigen and the variable 56-kilodalton antigen in scrub typhus patients
- PMID: 21508168
- PMCID: PMC3122618
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00017-11
Kinetics and magnitude of antibody responses against the conserved 47-kilodalton antigen and the variable 56-kilodalton antigen in scrub typhus patients
Abstract
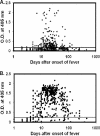
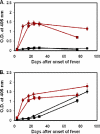
Western blot analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi whole-cell lysates with scrub typhus patient sera has identified at least five protein antigens of O. tsutsugamushi with molecular sizes of 22 kDa, 47 kDa, 56 kDa, 58 kDa, and 110 kDa. In this study, sera from serial bleedings of 108 patients were used to study the kinetics and the magnitude of specific antibody responses against the 47-kDa and 56-kDa antigens. Recombinant protein of the conserved 47-kDa antigen (r47b) or a mixture of truncated 56-kDa antigen (r56s) from three prototype strains was used as the antigen in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Our results showed that 76% and 93% of these patients had elevated IgM and IgG against r47b, respectively, and 98% and 100% had elevated IgM and IgG against r56s, respectively. The kinetics of antibody responses against r47b and r56s can be grouped into three patterns. In the first type of response, IgM and IgG against r47b and r56s appeared about the same time. The IgM and IgG titers against r56s were much higher than those against r47b. In the second type of response, induction of IgM appeared to be similar to that in the first type. The major difference to the first type is that the IgG titers against r47b were induced at least 1 week later than those against the r56s. The third type showed strong IgG responses against both r47b and r56s, and low or no IgM responses indicated a secondary infection. This is the first systematic investigation of antibody response kinetics against the conserved 47-kDa antigen versus the variable 56-kDa antigen in scrub typhus patients.
Figures




References
-
- Bourgeois A. L., et al. 1982. Humoral and cellular responses in scrub typhus patients reflecting primary infection and reinfection with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 31:532–540 - PubMed
-
- Brown G. W., Robinson D. M., Huxsoll D. L., Ng T. S., Lim K. J. 1976. Scrub typhus: a common cause of illness in indigenous populations. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 70:444–448 - PubMed
-
- Brown G. W., Robinson D. M., Huxsoll D. L. 1978. Serological evidence for a high incidence of transmission of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in two Orang Asli settlements in Peninsular Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 27:121–123 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

