A proactive mechanism for selective suppression of response tendencies
- PMID: 21508221
- PMCID: PMC3111595
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6292-10.2011
A proactive mechanism for selective suppression of response tendencies
Abstract
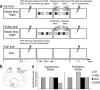
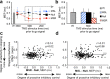
While most research on stopping action examines how an initiated response is stopped when a signal occurs (i.e., reactively), everyday life also calls for a mechanism to prepare to stop a particular response tendency (i.e., proactively and selectively). We hypothesized that human subjects can prepare to stop a particular response by proactively suppressing that response representation in the brain. We tested this by using single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation and concurrent electromyography. This allowed us to interrogate the corticomotor excitability of specific response representations even before action ensued. We found that the motor evoked potential of the effector that might need to be stopped in the future was significantly reduced compared with when that effector was at rest. Further, this neural index of proactive and selective suppression predicted the subsequent selectivity with which the behavioral response was stopped. These results go further than earlier reports of reduced motor excitability when responses are stopped. They show that the control can be applied in advance (proactively) and also targeted at a particular response channel (selectively). This provides novel evidence for an active mechanism of suppression in the brain that is setup according to the subject's goals and even before action ensues.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander GE, Crutcher MD, DeLong MR. Basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits: parallel substrates for motor, oculomotor, “prefrontal” and “limbic” functions. Prog Brain Res. 1990;85:119–146. - PubMed
-
- Aron AR. The neural basis of inhibition in cognitive control. Neuroscientist. 2007;13:214–228. - PubMed
-
- Aron AR, Verbruggen F. Stop the presses: dissociating a selective from a global mechanism for stopping. Psychol Sci. 2008;19:1146–1153. - PubMed
-
- Badry R, Mima T, Aso T, Nakatsuka M, Abe M, Fathi D, Foly N, Nagiub H, Nagamine T, Fukuyama H. Suppression of human cortico-motoneuronal excitability during the Stop-signal task. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120:1717–1723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
