Genomewide analysis of rat barrel cortex reveals time- and layer-specific mRNA expression changes related to experience-dependent plasticity
- PMID: 21508239
- PMCID: PMC6632955
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6514-10.2011
Genomewide analysis of rat barrel cortex reveals time- and layer-specific mRNA expression changes related to experience-dependent plasticity
Abstract
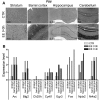
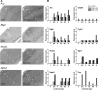
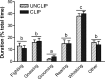
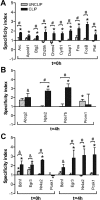
Because of its anatomical organization, the rodent whisker-to-barrel system is an ideal model to study experience-dependent plasticity. Manipulation of sensory input causes changes in the properties of the barrels at the physiological, structural, and functional levels. However, much less is known about the molecular events underlying these changes. To explore such molecular events, we have used a genomewide approach to identify key genes and molecular pathways involved in experience-induced plasticity in the barrel cortex of adult rats. Given the natural tendency of rats to explore novel objects, exposure to an enriched environment (EE) was used to stimulate the activity of the whisker-to-barrel cortex in vivo. Microarray analysis at two different time points after EE revealed differential expression of genes encoding transcription factors, including nuclear receptors, as well as of genes involved in the regulation of synaptic plasticity, cell differentiation, metabolism, and, surprisingly, blood vessel morphogenesis. These expression differences reflect changes in somatosensory information processing because unilateral whisker clipping showed EE-induced differential expression patterns in the spared versus deprived barrel cortex. Finally, in situ hybridization revealed cortical layer patterns specific for each selected gene. Together, the present study offers the first genomewide exploration of the key genes regulated by somatosensory stimulation in the barrel cortex and thus provides a solid experimental framework for future in-depth analysis of the mechanisms underlying experience-dependent plasticity.
Figures




References
-
- Ahissar E, Sosnik R, Haidarliu S. Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory thalamocortical pathway. Nature. 2000;406:302–306. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht C, von Der Kammer H, Mayhaus M, Klaudiny J, Schweizer M, Nitsch RM. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors induce the expression of the immediate early growth regulatory gene CYR61. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:28929–28936. - PubMed
-
- Bisler S, Schleicher A, Gass P, Stehle JH, Zilles K, Staiger JF. Expression of c-Fos, ICER, Krox-24 and JunB in the whisker-to-barrel pathway of rats: time course of induction upon whisker stimulation by tactile exploration of an enriched environment. J Chem Neuroanat. 2002;23:187–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
