Signaling-mediated cross-talk modulates swarming and biofilm formation in a coral pathogen Serratia marcescens
- PMID: 21509042
- PMCID: PMC3176518
- DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2011.45
Signaling-mediated cross-talk modulates swarming and biofilm formation in a coral pathogen Serratia marcescens
Abstract
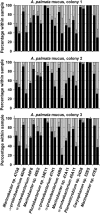
Interactions within microbial communities associated with marine holobionts contribute importantly to the health of these symbiotic organisms formed by invertebrates, dinoflagellates and bacteria. However, mechanisms that control invertebrate-associated microbiota are not yet fully understood. Hydrophobic compounds that were isolated from surfaces of asymptomatic corals inhibited biofilm formation by the white pox pathogen Serratia marcescens PDL100, indicating that signals capable of affecting the associated microbiota are produced in situ. However, neither the origin nor structures of these signals are currently known. A functional survey of bacteria recovered from coral mucus and from cultures of the dinoflagellate Symbiodinium spp. revealed that they could alter swarming and biofilm formation in S. marcescens. As swarming and biofilm formation are inversely regulated, the ability of some native α-proteobacteria to affect both behaviors suggests that the α-proteobacterial signal(s) target a global regulatory switch controlling the behaviors in the pathogen. Isolates of Marinobacter sp. inhibited both biofilm formation and swarming in S. marcescens PDL100, without affecting growth of the coral pathogen, indicative of the production of multiple inhibitors, likely targeting lower level regulatory genes or functions. A multi-species cocktail containing these strains inhibited progression of a disease caused by S. marcescens in a model polyp Aiptasia pallida. An α-proteobacterial isolate 44B9 had a similar effect. Even though ∼4% of native holobiont-associated bacteria produced compounds capable of triggering responses in well-characterized N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) biosensors, there was no strong correlation between the production of AHL-like signals and disruption of biofilms or swarming in S. marcescens.
Figures



References
-
- Alagely A, Rajamani S, Teplitski M. Luminescent reporters and their applications for the characterization of signals and signal-mimics that alter LasR-mediated quorum sensing. Method Mol Biol. 2011;692:113–130. - PubMed
-
- Bourne D, Iida Y, Uthicke S, Smith-Keune C. Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event. ISME J. 2008;2:350–363. - PubMed
-
- Brown BE, Bythell JC. Perspectives on mucus secretion in reef corals. Mar Ecol Progr Series. 2005;296:291–309.
-
- Cha C, Gao P, Chen YC, Shaw PD, Farrand SK. Production of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by gram-negative plant-associated bacteria. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998;11:1119–1129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

