Left-right patterning in the C. elegans embryo: Unique mechanisms and common principles
- PMID: 21509174
- PMCID: PMC3073266
- DOI: 10.4161/cib.4.1.14144
Left-right patterning in the C. elegans embryo: Unique mechanisms and common principles
Abstract
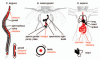
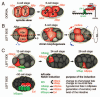
The development of bilateral symmetry during the evolution of species probably 600 million years ago brought about several important innovations: It fostered efficient locomotion, streamlining and favored the development of a central nervous system through cephalization. However, to increase their functional capacities, many organisms exhibit chirality by breaking their superficial left-right (l-r) symmetry, which manifests in the lateralization of the nervous system or the l-r asymmetry of internal organs. In most bilateria, the mechanisms that maintain consistent l-r asymmetry throughout development are poorly understood. This review highlights insights into mechanisms that couple early embryonic l-r symmetry breaking to subsequent l-r patterning in the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans. A recently identified strategy for l-r patterning in the early C. elegans embryo is discussed, the spatial separation of midline and anteroposterior axis, which relies on a rotational cellular rearrangement and non-canonical Wnt signaling. Evidence for a general relevance of rotational/torsional rearrangements during organismal l-r patterning and for non-canonical Wnt signaling/planar cell polarity as a common signaling mechanism to maintain l-r asymmetry is presented.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; embryonic development; left-right axis; planar cell polarity; symmetry breaking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Wnt signaling and planar cell polarity in left-right asymmetry.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023;153:181-193. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2023.01.008. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36967194
-
Diversity of left-right symmetry breaking strategy in animals.F1000Res. 2020 Feb 19;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-123. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.21670.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32148774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early embryonic programming of neuronal left/right asymmetry in C. elegans.Curr Biol. 2006 Dec 5;16(23):2279-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.041. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 17141609
-
Planar Asymmetries in the C. elegans Embryo Emerge by Differential Retention of aPARs at Cell-Cell Contacts.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Sep 27;7:209. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00209. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31612135 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical and Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Generates Molecular and Cellular Asymmetries to Establish Embryonic Axes.J Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 2;12(3):20. doi: 10.3390/jdb12030020. J Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39189260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rab GTPases are required for early orientation of the left-right axis in Xenopus.Mech Dev. 2013 Apr-May;130(4-5):254-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2012.11.007. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Mech Dev. 2013. PMID: 23354119 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and convergence in the mechanisms establishing L/R asymmetry in metazoa.EMBO Rep. 2014 Sep;15(9):926-37. doi: 10.15252/embr.201438972. Epub 2014 Aug 22. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 25150102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A unified model for left-right asymmetry? Comparison and synthesis of molecular models of embryonic laterality.Dev Biol. 2013 Jul 1;379(1):1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.03.021. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23583583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left-right asymmetry in the light of TOR: An update on what we know so far.Biol Cell. 2015 Sep;107(9):306-18. doi: 10.1111/boc.201400094. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25943139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurally Derived Tissues in Xenopus laevis Embryos Exhibit a Consistent Bioelectrical Left-Right Asymmetry.Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:353491. doi: 10.1155/2012/353491. Epub 2012 Dec 30. Stem Cells Int. 2012. PMID: 23346115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown NA, Wolpert L. The development of handedness in left/right asymmetry. Development. 1990;109:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Levin M, Mercola M. The compulsion of chirality: toward an understanding of left-right asymmetry. Genes Dev. 1998;12:763–769. - PubMed
-
- Cintas P. Chirality of living systems: a helping hand from crystals and oligopeptides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41:1139–1145. - PubMed
-
- Levin M. Left-right asymmetry in embryonic development: a comprehensive review. Mech Dev. 2005;122:3–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
