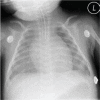
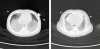
Acute Idiopathic Pulmonary Haemorrhage in a 2 month old Infant: Case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 21509296
- PMCID: PMC3074769
Acute Idiopathic Pulmonary Haemorrhage in a 2 month old Infant: Case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Pulmonary haemorrhage is usually secondary to a systemic disease affecting the lung with or without other organ involvement. Idiopathic pulmonary haemorrhage is a diagnosis of exclusion; as described in the literature, it is a rare disease. We report a two months old infant who presented at the Emergency Department of Sultan Qaboos University Hospital, Oman, with respiratory failure and shock secondary to an acute severe pulmonary haemorrhage. Detailed investigations for pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal and systemic inflammatory causes were negative. His clinical presentation and radiological imaging were consistent with idiopathic pulmonary haemorrhage. Treatment with corticosteroids resulted in a remarkable and fast recovery from his critical respiratory status.
Keywords: Case report; Corticosteroids; Haemosiderosis; Oman; Respiratory failure; Shock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cor Triatriatum Sinistrum: A rare disease with a common presentation.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2021 May;21(2):e324-e326. doi: 10.18295/squmj.2021.21.02.026. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2021. PMID: 34221485 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis in adults: a case report and review of the literature.Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:267857. doi: 10.1155/2012/267857. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Case Rep Med. 2012. PMID: 22851975 Free PMC article.
-
Early diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis: increased haemosiderin-laden macrophages in repeat bronchoscopy.Respirol Case Rep. 2018 Feb 7;6(3):e00304. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.304. eCollection 2018 Apr. Respirol Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29541474 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospirosis with pulmonary haemorrhage and multiple organ failure: a case report and literature review.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211019665. doi: 10.1177/03000605211019665. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34044641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis revisited.Eur Respir J. 2004 Jul;24(1):162-70. doi: 10.1183/09031936.04.00116302. Eur Respir J. 2004. PMID: 15293620 Review.
Cited by
-
Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemorrhage in Infancy: A Case Report and Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;13(7):1270. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13071270. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coss-Bu JA, Sachdeva RC, Bricker JT, Harrison GM, Jefferson LS. Hemoptysis: a 10-year retrospective study. Pediatrics. 1997;100:E7. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey S. Pulmonary hemorrhage/hemoptysis in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004;37:476–84. - PubMed
-
- Dearborn DG, Smith PG, Dahms BB, Allan TM, Sorenson WG, Montana E, et al. Clinical profile of 30 infants with acute pulmonary hemorrhage in Cleveland. Pediatrics. 2002;110:627–37. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Investigation of acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage among infants in Massachusetts, December 2002–June 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004;53:817–20. - PubMed
-
- Kjellman B, Elinder G, Garwicz S, Svan H. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis in Swedish children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984;73:584–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources