Potentiation and overshadowing between landmarks and environmental geometric cues
- PMID: 21509462
- PMCID: PMC4231293
- DOI: 10.3758/s13420-011-0032-8
Potentiation and overshadowing between landmarks and environmental geometric cues
Abstract
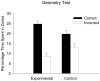
Rats were required in three experiments to find one of two submerged platforms that were situated in the same pair of diagonally opposite corners of a rectangular grey swimming pool. The experimental groups were trained with landmarks, comprising A4 cards attached to the walls, located in the corners containing the platforms. For the control groups, the landmarks were situated in the corners containing the platforms for half of the trials, and in the other corners for the remaining trials. Learning about the positions of the platforms with reference to the shape of the pool was overshadowed in the experimental groups when the landmarks were white, and enhanced when the landmarks were black. A fourth experiment assessed whether geometric cues influenced the control acquired by the landmarks. As in the previous experiments, the presence of the geometric cues overshadowed learning about the landmarks when they were white, but enhanced learning when the landmarks were black.
Figures
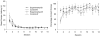
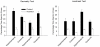

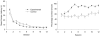


Similar articles
-
Absence of an interaction between navigational strategies based on local and distal landmarks.J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2004 Jan;30(1):34-44. doi: 10.1037/0097-7403.30.1.34. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2004. PMID: 14709113
-
Overshadowing of geometry learning by discrete landmarks in the water maze: effects of relative salience and relative validity of competing cues.J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2013 Apr;39(2):126-39. doi: 10.1037/a0031199. Epub 2013 Feb 18. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2013. PMID: 23421399
-
Potentiation, overshadowing, and blocking of spatial learning based on the shape of the environment.J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2006 Jul;32(3):201-14. doi: 10.1037/0097-7403.32.3.201. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2006. PMID: 16834489
-
Whither geometry? Troubles of the geometric module.Trends Cogn Sci. 2008 Sep;12(9):355-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Trends Cogn Sci. 2008. PMID: 18684662 Review.
-
Spatial reorientation in large and small enclosures: comparative and developmental perspectives.Cogn Process. 2008 Dec;9(4):229-38. doi: 10.1007/s10339-008-0202-6. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Cogn Process. 2008. PMID: 18196304 Review.
Cited by
-
Asymmetry in the discrimination of length during spatial learning.J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2013 Oct;39(4):342-56. doi: 10.1037/a0032570. Epub 2013 May 13. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2013. PMID: 23668184 Free PMC article.
-
What makes a landmark effective? Sex differences in a navigation task.Learn Behav. 2014 Dec;42(4):348-56. doi: 10.3758/s13420-014-0152-z. Learn Behav. 2014. PMID: 25169581
-
Overshadowing of geometric cues by a beacon in a spatial navigation task.Learn Behav. 2013 Jun;41(2):179-91. doi: 10.3758/s13420-012-0096-0. Learn Behav. 2013. PMID: 23180188
-
Distinct and combined responses to environmental geometry and features in a working-memory reorientation task in rats and chicks.Sci Rep. 2020 May 5;10(1):7508. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64366-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32371918 Free PMC article.
-
Learned predictiveness training modulates biases towards using boundary or landmark cues during navigation.Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2015;68(6):1183-202. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2014.977925. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2015. PMID: 25409751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bingman VP, Erichsen JT, Anderson JD, Good MA, Pearce JM. Spared feature-structure discrimination but diminished salience of environmental geometry in hippocampal-lesioned homing pigeons (Columbia livia) Behavioral Neuroscience. 2006;120:835–841. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME, Dunlap CM, Swartzentruber D. Potentiation of tast by another taste during compound aversion learning. Animal Learning & Behavior. 1987;15:433–438.
-
- Cheng K. A purely geometric module in the rats spatial representation. Cognition. 1986;23:149–178. - PubMed
-
- Durlach PJ, Rescorla RS. Potentiation rather than overshadowing in odor-aversion learning: An analysis in terms of within-compound associations. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 1980;6:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Gallistel CR. The Organization of Learning. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1990.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

