Association of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism with magnetic resonance spectroscopic markers in the human hippocampus: in vivo evidence for effects on the glutamate system
- PMID: 21509595
- PMCID: PMC3270260
- DOI: 10.1007/s00406-011-0214-6
Association of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism with magnetic resonance spectroscopic markers in the human hippocampus: in vivo evidence for effects on the glutamate system
Abstract
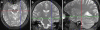
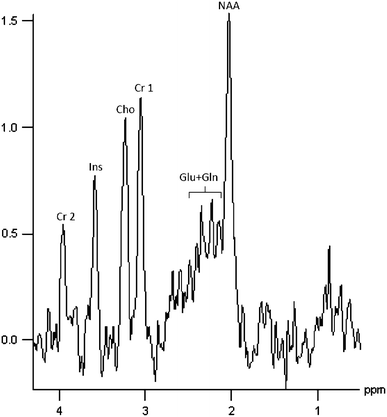
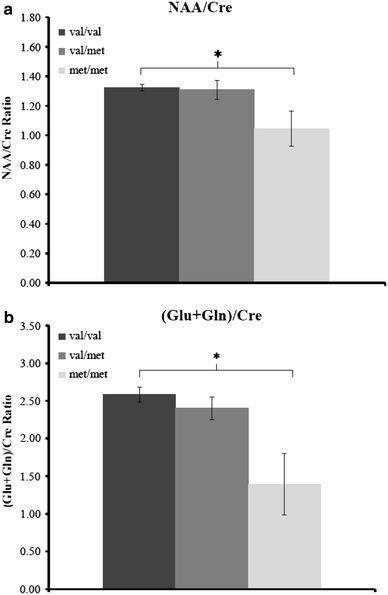
The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key regulator of synaptic plasticity and has been suggested to be involved in the pathophysiology and pathogenesis of psychotic disorders, with particular emphasis on dysfunctions of the hippocampus. The aim of the present study was to replicate and to extend prior findings of BDNF val66met genotype effects on hippocampal volume and N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) levels. Hundred and fifty-eight caucasians (66 schizophrenic, 45 bipolar, and 47 healthy subjects; 105 subjects underwent MRI and 103 MRS scanning) participated in the study and were genotyped with regard to the val66met polymorphism (rs6265) of the BDNF gene. Hippocampal volumes were determined using structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and measures of biochemical markers were taken using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy ((1)H-MRS) in the hippocampus and other brain regions. Verbal memory was assessed as a behavioral index of hippocampal function. BDNF genotype did not impact hippocampal volumes. Significant genotype effects were found on metabolic markers specifically in the left hippocampus. In particular, homozygous carriers of the met-allele exhibited significantly lower NAA/Cre and (Glu + Gln)/Cre metabolic ratios compared with val/val homozygotes, independently of psychiatric diagnoses. BDNF genotype had a numerical, but nonsignificant effect on verbal memory performance. These findings provide first in vivo evidence for an effect of the functional BDNF val66met polymorphism on the glutamate system in human hippocampus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism on levels of hippocampal N-acetyl-aspartate assessed by magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging at 3 Tesla.Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Nov 15;64(10):856-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.07.009. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18707679 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive and magnetic resonance imaging brain morphometric correlates of brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met gene polymorphism in patients with schizophrenia and healthy volunteers.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Jul;63(7):731-40. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.7.731. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16818862 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced hippocampus volume and memory performance in bipolar disorder patients carrying the BDNF val66met met allele.J Affect Disord. 2016 Jul 1;198:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.03.044. Epub 2016 Mar 10. J Affect Disord. 2016. PMID: 27018938 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and hippocampal volume in neuropsychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Aug;55:107-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 May 5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25956254
-
The association of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and the hippocampal volumes in healthy humans: a joint meta-analysis of published and new data.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014 May;42:267-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.03.011. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014. PMID: 24674929 Review.
Cited by
-
Schizophrenia: brain morphology and treatment aspects.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013 Feb;263(1):1-2. doi: 10.1007/s00406-012-0388-6. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23306379 No abstract available.
-
Relationship between Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Schneiderian First Rank Symptoms in Antipsychotic-Naïve Schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Jul 2;4:64. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00064. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23847552 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental regulation of expression of schizophrenia susceptibility genes in the primate hippocampal formation.Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Oct 23;2(10):e173. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.105. Transl Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23092977 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor and dynamics of the seizure threshold of electroconvulsive therapy.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017 Dec;267(8):787-794. doi: 10.1007/s00406-016-0744-z. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27787610
-
Risk-Conferring Glutamatergic Genes and Brain Glutamate Plus Glutamine in Schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 12;8:79. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00079. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28659829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aicardi G, Argilli E, Cappello S, Santi S, Riccio M, Thoenen H, Canossa M. Induction of long-term potentiation and depression is reflected by corresponding changes in secretion of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:15788–15792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406960101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

