Adaptive noise cancellation to suppress electrocardiography artifacts during real-time interventional MRI
- PMID: 21509878
- PMCID: PMC3080760
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.22530
Adaptive noise cancellation to suppress electrocardiography artifacts during real-time interventional MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a system for artifact suppression in electrocardiogram (ECG) recordings obtained during interventional real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
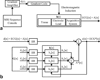
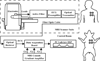
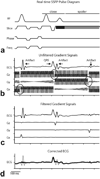
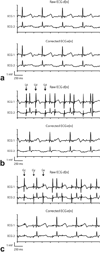
Materials and methods: We characterized ECG artifacts due to radiofrequency pulses and gradient switching during MRI in terms of frequency content. A combination of analog filters and digital least mean squares adaptive filters were used to filter the ECG during in vivo experiments and the results were compared with those obtained with simple low-pass filtering. The system performance was evaluated in terms of artifact suppression and ability to identify arrhythmias during real-time MRI.
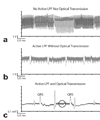
Results: Analog filters were able to suppress artifacts from high-frequency radiofrequency pulses and gradient switching. The remaining pulse artifacts caused by intermittent preparation sequences or spoiler gradients required adaptive filtering because their bandwidth overlapped with that of the ECG. Using analog and adaptive filtering, a mean improvement of 38 dB (n = 11, peak QRS signal to pulse artifact noise) was achieved. This filtering system was successful in removing pulse artifacts that obscured arrhythmias such as premature ventricular complexes and complete atrioventricular block.
Conclusion: We have developed an online ECG monitoring system employing digital adaptive filters that enables the identification of cardiac arrhythmias during real-time MRI-guided interventions.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Birkholz T, Schmid M, Nimsky C, Schüttler J, Schmitz B. ECG artifacts during intraoperative high-field MRI scanning. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology. 2004;16(4):271. - PubMed
-
- Felblinger J, Lehmann C, Boesch C. Electrocardiogram acquisition during MR examinations for patient monitoring and sequence triggering. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1994;32(4):523–529. - PubMed
-
- Allen P, Polizzi G, Krakow K, Fish D, Lemieux L. Identification of EEG events in the MR scanner: the problem of pulse artifact and a method for its subtraction. Neuroimage. 1998;8(3):229–239. - PubMed
-
- Nijm G, Swiryn S, Larson A, Sahakian A. Extraction of the magnetohydrodynamic blood flow potential from the surface electrocardiogram in magnetic resonance imaging. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing. 2008;46(7):729–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

