Organization and function of the FKBP52 and FKBP51 genes
- PMID: 21514887
- PMCID: PMC3156272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2011.03.013
Organization and function of the FKBP52 and FKBP51 genes
Abstract
Best established as components of steroid hormone receptor complexes, it is now clear that the large molecular weight immunophilins, FKBP52 and FKBP51, play important regulatory roles elsewhere in the cell. This review outlines what is known about the organization of the genes, FKBP4 and FKBP5, respectively, encoding these proteins and describes their diverse actions in the nervous system, reproduction, and cancer. The organization of FKBP4 and FKBP5 is very similar among the chordates, and gene expression is influenced by both genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Recent studies identifying roles of FKBP52 and FKBP51 in the regulation of the microtubule-associated protein tau and microtubule assembly are discussed, as is their interaction with and influence on the transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) subfamily of ion channel proteins.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

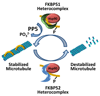
References
-
- Galat A. Functional drift of sequence attributes in the FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs) J Chem Inf Model. 2008;48:1118–1130. - PubMed
-
- Massol N, Lebeau MC, Schumacher M, Baulieu EE. Promoter activity and gene structure of rabbit FKBP52. DNA Cell Biol. 2003;22:505–511. - PubMed
-
- Scammell JG, Hubler TR, Denny WB, Valentine DL. Organization of the human FK506-binding immunophilin FKBP52 protein gene (FKBP4) Genomics. 2003;81:640–643. - PubMed
-
- Scammell JG, Denny WB, Valentine DL, Smith DF. Overexpression of the FK506-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is the common cause of glucocorticoid resistance in three New World primates. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2001;124:152–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

