Enhanced antigen processing of flagellin fusion proteins promotes the antigen-specific CD8+ T cell response independently of TLR5 and MyD88
- PMID: 21515787
- PMCID: PMC3743533
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001855
Enhanced antigen processing of flagellin fusion proteins promotes the antigen-specific CD8+ T cell response independently of TLR5 and MyD88
Abstract
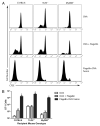
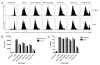
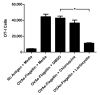
Flagellin is a highly effective adjuvant for CD4(+) T cell and humoral immune responses. However, there is conflicting data in the literature regarding the ability of flagellin to promote a CD8(+) T cell response. In this article, we report that immunization of wild-type, TLR5(-/-), and MyD88(-/-) adoptive transfer recipient mice revealed the ability of flagellin fusion proteins to promote OVA-specific CD8(+) T cell proliferation independent of TLR5 or MyD88 expression by the recipient animal. Wild-type and TLR5(-/-) APCs were able to stimulate high levels of OVA-specific CD8(+) T cell proliferation in vitro in response to a flagellin fusion protein containing full-length OVA or the SIINFEKL epitope and 10 flanking amino acids (OVAe), but not to OVA and flagellin added as separate proteins. This effect was independent of the conserved regions of flagellin and occurred in response to OVAe alone. Comparison of IFN-γ production by CD8(+) effector cells revealed higher levels of SIINFEKL peptide-MHC I complexes on the surface of APCs that had been pulsed with OVAe-flagellin fusion proteins than on cells pulsed with OVA. Inhibition of the proteasome significantly reduced Ag-specific proliferation in response to OVAe fusion proteins. In summary, our data are consistent with the conclusion that flagellin-OVA fusion proteins induce an epitope-specific CD8(+) T cell response by facilitating Ag processing and not through stimulatory signaling via TLR5 and MyD88. Our findings raise the possibility that flagellin might be an efficient Ag carrier for Ags that are poorly processed in their native state.
Figures

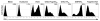
References
-
- Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ, Madara JL. Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression. J. Immunol. 2001;167:1882–1885. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 2001;410:1099–1103. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly MA, Steiner TS. Two nonadjacent regions in enter-oaggregative Escherichia coli flagellin are required for activation of toll-like receptor 5. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:40456–40461. - PubMed
-
- Mizel SB, Snipes JA. Gram-negative flagellin-induced self-tolerance is associated with a block in interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase release from toll-like receptor 5. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:22414–22420. - PubMed
-
- McEwen J, Levi R, Horwitz RJ, Arnon R. Synthetic recombinant vaccine expressing influenza haemagglutinin epitope in Salmonella flagellin leads to partial protection in mice. Vaccine. 1992;10:405–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

