Mesothelin overexpression promotes autocrine IL-6/sIL-6R trans-signaling to stimulate pancreatic cancer cell proliferation
- PMID: 21515913
- PMCID: PMC3128561
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgr075
Mesothelin overexpression promotes autocrine IL-6/sIL-6R trans-signaling to stimulate pancreatic cancer cell proliferation
Abstract
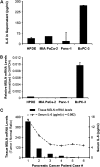
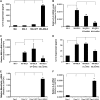
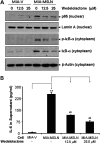
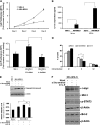
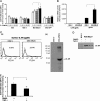
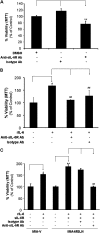
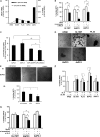
Mesothelin (MSLN) overexpression in pancreatic cancer (PC) leads to enhanced cell survival/proliferation and tumor progression. After screening for a number of growth factors/cytokines, we found that the MSLN expression correlated closely with interleukin (IL)-6 in human PC specimens and cell lines. Stably overexpressing MSLN in different PC cell lines (MIA-MSLN and Panc1-MSLN) led to higher IL-6 production. Silencing MSLN by small interfering RNA (siRNA) significantly reduced IL-6 levels. Blocking the observed constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) with IKK inhibitor wedelolactone in MIA-MSLN cells also reduced IL-6. Silencing IL-6 by siRNA reduced cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and induced apoptosis with significant decrease of c-myc/bcl-2. Interestingly, recombinant IL-6-induced proliferation of MIA-MSLN cells but not MIA-V cells. Although messenger RNA/protein levels of IL-6R did not vary, soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) was significantly elevated in MIA-MSLN and was reduced by treatment with the TACE/ADAM17 inhibitor TAPI-1, indicating intramembrane IL-6R cleavage and IL-6 trans-signaling may be operative in MIA-MSLN cells. Blocking the IL-6/sIL-6R axis using sIL-6R antibody abrogated basal proliferation/survival as well as recombinant human IL-6-induced cell proliferation. Our data suggest that MSLN-activated NF-κB induces elevated IL-6 expression, which acts as a growth factor to support PC cell survival/proliferation through a novel auto/paracrine IL-6/sIL-6R trans-signaling. In addition, using a panel of PC cells with varying MSLN/IL-6 expressions, we showed that MSLN/IL-6 axis is a major survival axis in PC supporting tumor cell growth under anchorage-dependent and independent conditions. The close correlation between MSLN and IL-6 provides a new rationale for combination therapy for effective control of MSLN-overexpressing PCs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesothelin confers pancreatic cancer cell resistance to TNF-α-induced apoptosis through Akt/PI3K/NF-κB activation and IL-6/Mcl-1 overexpression.Mol Cancer. 2011 Aug 31;10:106. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-106. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21880146 Free PMC article.
-
Mesothelin-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation involves alteration of cyclin E via activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription protein 3.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Nov;6(11):1755-65. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0095. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19010822 Free PMC article.
-
A tumorigenic factor interactome connected through tumor suppressor microRNA-198 in human pancreatic cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 1;19(21):5901-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3776. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23989979 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 trans-signalling directly induces RANKL on fibroblast-like synovial cells and is involved in RANKL induction by TNF-alpha and IL-17.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008 Nov;47(11):1635-40. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken363. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008. PMID: 18786965
-
Interleukin-6 in bone metastasis and cancer progression.Eur J Cancer. 2010 May;46(7):1223-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.026. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Eur J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20335016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel 89Zr-labeled DDS Device Utilizing Human IgG Variant (scFv): "Lactosome" Nanoparticle-Based Theranostics for PET Imaging and Targeted Therapy.Life (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;11(2):158. doi: 10.3390/life11020158. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphisms of an oncogenic gene, mesothelin, predict the risk and prognosis of gastric cancer in a Chinese Han population.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Jul;96(7):2097-2111. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03290-6. Epub 2022 Apr 9. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35396937
-
From Malignant Progression to Therapeutic Targeting: Current Insights of Mesothelin in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 6;21(11):4067. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114067. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32517181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-ERC/mesothelin provokes lymphatic invasion of colorectal adenocarcinoma.J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan;49(1):81-92. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0773-6. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 23512344
-
Enhanced Expression of Glycolytic Enzymes and Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex Flavoprotein Subunit A by Mesothelin Promotes Glycolysis and Mitochondrial Respiration in Myeloblasts of Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 10;25(4):2140. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042140. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hassan R, et al. Mesothelin: a new target for immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004;10:3937–3942. - PubMed
-
- Uehara N, et al. Mesothelin promotes anchorage-independent growth and prevents anoikis via extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008;6:186–193. - PubMed
-
- Adachi Y, et al. Interleukin-6 induces both cell growth and VEGF production in malignant mesotheliomas. Int. J. Cancer. 2006;119:1303–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

