Reelin, Rap1 and N-cadherin orient the migration of multipolar neurons in the developing neocortex
- PMID: 21516100
- PMCID: PMC3102785
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2816
Reelin, Rap1 and N-cadherin orient the migration of multipolar neurons in the developing neocortex
Abstract
Projection neurons migrate from the ventricular zone to the neocortical plate during the development of the mouse brain. Their overall movement is radial, but they become multipolar and move nonradially in the intermediate zone. Here we show that Reelin, the Rap1 GTPase and N-cadherin (NCad) are important for multipolar neurons to polarize their migration toward the cortical plate. Inhibition and rescue experiments indicated that Reelin regulates migration through Rap1 and Akt, and that the Rap1-regulated GTPases RalA, RalB, Rac1 and Cdc42 are also involved. We found that Rap1 regulated the plasma membrane localization of NCad and NCad rescued radial polarization when Rap1 was inhibited. However, inhibition of Rap1 or NCad had little effect on glia-dependent locomotion. We propose a multistep mechanism in which Reelin activates Rap1, Rap1 upregulates NCad, and NCad is needed to orient cell migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


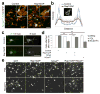

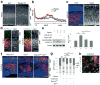
References
-
- Bielas S, Higginbotham H, Koizumi H, Tanaka T, Gleeson JG. Cortical neuronal migration mutants suggest separate but intersecting pathways. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:593–618. - PubMed
-
- Noctor SC, Martinez-Cerdeno V, Ivic L, Kriegstein AR. Cortical neurons arise in symmetric and asymmetric division zones and migrate through specific phases. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:136–44. - PubMed
-
- Nadarajah B, Brunstrom JE, Grutzendler J, Wong RO, Pearlman AL. Two modes of radial migration in early development of the cerebral cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:143–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

