Individual patient data meta-analysis of randomized trials evaluating IL-2 monotherapy as remission maintenance therapy in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 21518931
- PMCID: PMC3539044
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-337725
Individual patient data meta-analysis of randomized trials evaluating IL-2 monotherapy as remission maintenance therapy in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
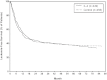
IL-2 is a natural, T cell-derived cytokine that stimulates the cytotoxic functions of T and natural killer cells. IL-2 monotherapy has been evaluated in several randomized clinical trials (RCTs) for remission maintenance in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete remission (CR1), and none demonstrated a significant benefit of IL-2 monotherapy. The objective of this meta-analysis was to reliably determine IL-2 efficacy by combining all available individual patient data (IPD) from 5 RCTs (N = 905) and summary data from a sixth RCT (N = 550). Hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated using Cox regression models stratified by trial, with HR < 1 indicating treatment benefit. Combined IPD showed no benefit of IL-2 over no treatment in terms of leukemia-free survival (HR = 0.97; P = .74) or overall survival (HR = 1.08; P = .39). Analyses including the sixth RCT yielded qualitatively identical results (leukemia-free survival HR = 0.96, P = .52; overall survival HR = 1.06; P = .46). No significant heterogeneity was found between the trials. Prespecified subset analyses showed no interaction between the lack of IL-2 effect and any factor, including age, sex, baseline performance status, karyotype, AML subtype, and time from achievement of CR1 to initiation of maintenance therapy. We conclude that IL-2 alone is not an effective remission maintenance therapy for AML patients in CR1.
Figures



References
-
- Rowe JM, Xiaochun L, Cassileth PA, et al. Very poor survival of patients with AML who relapse after achieving a first complete remission: The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group experience [abstract]. Blood. 2005;106(11):546.
-
- Romero AI, Thoren FB, Aurelius J, et al. Post-consolidation immunotherapy with histamine dihydrochloride and interleukin-2 in AML. Scand J Immunol. 2009;70(3):194–205. - PubMed
-
- Krug U, Lubbert M, Buchner T. Maintenance therapy in acute myeloid leukemia revisited: will new agents rekindle an old interest? Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(2):85–90. - PubMed
-
- Blaise D, Olive D, Michallet M, et al. Impairment of leukaemia-free survival by addition of interleukin-2-receptor antibody to standard graft-versus-host prophylaxis. Lancet. 1995;345(8958):1144–1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

