Kinase suppressor of ras 1 (KSR1) regulates PGC1α and estrogen-related receptor α to promote oncogenic Ras-dependent anchorage-independent growth
- PMID: 21518958
- PMCID: PMC3133429
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.05255-11
Kinase suppressor of ras 1 (KSR1) regulates PGC1α and estrogen-related receptor α to promote oncogenic Ras-dependent anchorage-independent growth
Abstract
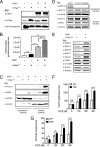
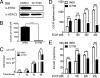
Kinase suppressor of ras 1 (KSR1) is a molecular scaffold of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) cascade that enhances oncogenic Ras signaling. Here we show KSR1-dependent, but ERK-independent, regulation of metabolic capacity is mediated through the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α (PGC1α) and estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα). This KSR1-regulated pathway is essential for the transformation of cells by oncogenic Ras. In mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) expressing H-Ras(V12), ectopic PGC1α was sufficient to rescue ERRα expression, metabolic capacity, and anchorage-independent growth in the absence of KSR1. The ability of PGC1α to promote anchorage-independent growth required interaction with ERRα, and treatment with an inhibitor of ERRα impeded anchorage-independent growth. In contrast to PGC1α, the expression of constitutively active ERRα (CA-ERRα) was sufficient to enhance metabolic capacity but not anchorage-independent growth in the absence of KSR1. These data reveal KSR1-dependent control of PGC1α- and ERRα-dependent pathways that are necessary and sufficient for signaling by oncogenic H-Ras(V12) to regulate metabolism and anchorage-independent growth, providing novel targets for therapeutic intervention.
Figures


References
-
- Baracca A., et al. 2010. Mitochondrial complex I decrease is responsible for bioenergetic dysfunction in K-ras transformed cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1797: 314–323 - PubMed
-
- Blum R., Jacob-Hirsch J., Amariglio N., Rechavi G., Kloog Y. 2005. Ras inhibition in glioblastoma down-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, causing glycolysis shutdown and cell death. Cancer Res. 65: 999–1006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
