Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture : A Severe Canal Compromise But Neurologically Intact Case
- PMID: 21519504
- PMCID: PMC3079100
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2011.49.2.128
Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture : A Severe Canal Compromise But Neurologically Intact Case
Abstract
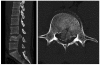
The low lumbar spine is deeply located in flexible segments, and has a physiologic lordosis. Therefore, burst fractures of the low lumbar spine are uncommon injuries. The treatment for such injuries may either be conservative or surgical management according to canal compromise and the neurological status. However, there are no general guidelines or consensus for the treatment of low lumbar burst fractures especially in neurologically intact cases with severe canal compromise. We report a patient with a burst fracture of the fourth lumbar vertebra, who was treated surgically but without fusion because of the neurologically intact status in spite of severe canal compromise of more than 85%. It was possible to preserve motion segments by removal of screws at one year later. We also discuss why bone fusion was not necessary with review of the relevant literature.
Keywords: Burst fracture; Fusion; Low lumbar spine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Unstable Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Burst Fracture : A Prospective Study on Selective Consecutive Patients.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012 Apr;51(4):203-7. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.4.203. Epub 2012 Apr 30. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012. PMID: 22737299 Free PMC article.
-
Mono segmental fixation of selected types of thoracic and lumbar fractures; a prospective study.Int Orthop. 2016 Jun;40(6):1083-9. doi: 10.1007/s00264-016-3152-0. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Int Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26987982
-
Is fusion necessary for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine?: a prospective, randomized study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006 Nov 1;31(23):2646-52; discussion 2653. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000244555.28310.40. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006. PMID: 17077731 Clinical Trial.
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Evaluation and Treatment of Patients With Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: Nonoperative Care.Neurosurgery. 2019 Jan 1;84(1):E46-E49. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy369. Neurosurgery. 2019. PMID: 30203096
-
Isolated unstable burst fractures of the fifth lumbar vertebra: functional and radiological outcome after posterior stabilization with reconstruction of the anterior column: About 6 cases and literature review.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020 Oct;106(6):1215-1220. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.03.014. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32354682 Review.
Cited by
-
Short segment screw fixation without fusion in treatment for unstable thoracolumbar burst fracture.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Dec 15;7(12):5681-5. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25664090 Free PMC article.
-
Missed Cauda Equina Syndrome after Burst Fracture of the Lumbar Spine.Korean J Neurotrauma. 2015 Oct;11(2):175-9. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.2.175. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2015. PMID: 27169089 Free PMC article.
-
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Unstable Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Burst Fracture : A Prospective Study on Selective Consecutive Patients.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012 Apr;51(4):203-7. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.4.203. Epub 2012 Apr 30. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012. PMID: 22737299 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: Commentary on In-Fracture Pedicular Screw Placement During Ligamentotaxis Following Traumatic Spine Injuries, a Randomized Clinical Trial on Outcomes (Korean J Neurotrauma 2023;19:90-102).Korean J Neurotrauma. 2023 Jun 19;19(2):268-269. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2023.19.e22. eCollection 2023 Jun. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2023. PMID: 37431374 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Implant removal after percutaneous short segment fixation for thoracolumbar burst fracture : does it preserve motion?J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014 Feb;55(2):73-7. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.2.73. Epub 2014 Feb 28. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014. PMID: 24653799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An HS, Simpson JM, Ebraheim NA, Jackson WT, Moore J, O'Malley NP. Low lumbar burst fractures: comparison between conservative and surgical treatments. Orthopedics. 1992;15:367–373. - PubMed
-
- Chan DP, Seng NK, Kaan KT. Nonoperative treatment in burst fractures of the lumbar spine (L2-L5) without neurologic deficits. Spine. 1993;18:320–325. - PubMed
-
- de Klerk LW, Fontijne WP, Stijnen T, Braakman R, Tanghe HL, van Linge B. Spontaneous remodeling of the spinal canal after conservative management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine. 1998;23:1057–1060. - PubMed
-
- el Masry WS, Short DJ. Current concept: spinal injuries and rehabilitation. Curr Opin Neurol. 1997;10:484–492. - PubMed
-
- Finn CA, Stauffer ES. Burst fractures of the fifth vertebra. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:398–403. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

