Impact of sphingomyelin levels on coronary heart disease and left ventricular systolic function in humans
- PMID: 21521522
- PMCID: PMC3111338
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-8-25
Impact of sphingomyelin levels on coronary heart disease and left ventricular systolic function in humans
Abstract
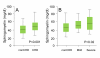
Sphingomyelin (SM) is an abundant phospholipid in cell membranes and in lipoproteins. In human plasma, SM is mainly found in atherogenic lipoproteins; therefore, higher levels of SM may promote atherogenesis. We investigated the relations between plasma SM levels and the presence of angiographic coronary heart disease (CHD) and left ventricular systolic dysfunction. We studied 732 patients referred for coronary angiography. Median SM levels were higher among patients with CHD and in those with LV systolic dysfunction (LVEF<50%) than in patients without CHD or LV dysfunction. SM levels were significantly correlated with fibrinogen levels, diabetes, apoB, and triglyceride levels. On multivariate analyses, higher median SM levels were associated with a higher risk of CHD and lower LV ejection fraction. The pro-atherogenic property of plasma SM might be related to 1) CHD; 2) LV systolic dysfunction; and 3) metabolism of apoB-containing or triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.
Figures
References
-
- Nilsson A, Duan RD. Absorption and lipoprotein transport of sphingomyelin. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:154–171. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez JL, Ghiselli GC, Torreggiani D, Sirtori CR. Very low density lipoproteins in normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits: lipid and protein composition and metabolism. Part 1. Chemical composition of very low density lipoproteins in rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1976;23:73–83. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90119-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zilversmit DB, Mc CE, Jordan PH, Henly WS, Ackerman RF. The synthesis of phospholipids in human atheromatous lesions. Circulation. 1961;23:370–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous