Development of a MR-visible compound for tracing neuroanatomical connections in vivo
- PMID: 21521610
- PMCID: PMC3419536
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.03.010
Development of a MR-visible compound for tracing neuroanatomical connections in vivo
Abstract
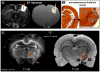
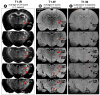
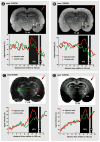
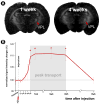
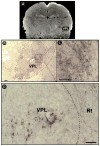
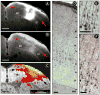
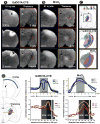
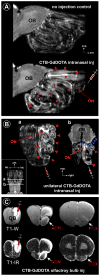
Traditional studies of neuroanatomical connections require injection of tracer compounds into living brains, then histology of the postmortem tissue. Here, we describe and validate a compound that reveals neuronal connections in vivo, using MRI. The classic anatomical tracer CTB (cholera-toxin subunit-B) was conjugated with a gadolinium-chelate to form GdDOTA-CTB. GdDOTA-CTB was injected into the primary somatosensory cortex (S1) or the olfactory pathway of rats. High-resolution MR images were collected at a range of time points at 11.7T and 7T. The transported GdDOTA-CTB was visible for at least 1 month post-injection, clearing within 2 months. Control injections of non-conjugated GdDOTA into S1 were not transported and cleared within 1-2 days. Control injections of Gd-Albumin were not transported either, clearing within 7 days. These MR results were verified by classic immunohistochemical staining for CTB, in the same animals. The GdDOTA-CTB neuronal transport was target specific, monosynaptic, stable for several weeks, and reproducible.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akers RM, Killackey HP. Organization of corticocortical connections in the parietal cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978;181:513–537. - PubMed
-
- Alitto HJ, Usrey WM. Corticothalamic feedback and sensory processing. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:440–445. - PubMed
-
- Angelucci A, Clasca F, Sur M. Anterograde axonal tracing with the subunit B of cholera toxin: a highly sensitive immunohistochemical protocol for revealing fine axonal morphology in adult and neonatal brains. J Neurosci Methods. 1996;65:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Aoki I, Naruse S, Tanaka C. Manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MEMRI) of brain activity and applications to early detection of brain ischemia. NMR Biomed. 2004;17:569–580. - PubMed
-
- Aoki I, Tanaka C, Takegami T, Ebisu T, Umeda M, Fukunaga M, Fukuda K, Silva AC, Koretsky AP, Naruse S. Dynamic activity-induced manganese-dependent contrast magnetic resonance imaging (DAIM MRI) Magn Reson Med. 2002;48:927–933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

