Metabolic sensing and the brain: who, what, where, and how?
- PMID: 21521751
- PMCID: PMC3192421
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-0194
Metabolic sensing and the brain: who, what, where, and how?
Abstract
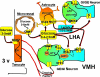
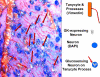
Unique subpopulations of specialized metabolic sensing neurons reside in a distributed network throughout the brain and respond to alterations in ambient levels of various metabolic substrates by altering their activity. Variations in local brain substrate levels reflect their transport across the blood- and cerebrospinal-brain barriers as well as local production by astrocytes. There are a number of mechanisms by which such metabolic sensing neurons alter their activity in response to changes in substrate levels, but it is clear that these neurons cannot be considered in isolation. They are heavily dependent on astrocyte and probably tanycyte metabolism and function but also respond to hormones (e.g. leptin and insulin) and cytokines that cross the blood-brain barrier from the periphery as well as hard-wired neural inputs from metabolic sensors in peripheral sites such as the hepatic portal vein, gastrointestinal tract, and carotid body. Thus, these specialized neurons are capable of monitoring and integrating multiple signals from the periphery as a means of regulating peripheral energy homeostasis.
Figures
References
-
- Mayer J. 1953. Glucostatic mechanism of regulation of food intake. N Engl J Med 249:13–16 - PubMed
-
- Anand BK, Chhina GS, Sharma KN, Dua S, Singh B. 1964. Activity of single neurons in the hypothalamus feeding centers: effect of glucose. Am J Physiol 207:1146–1154 - PubMed
-
- Oomura Y, Kimura K, Ooyama H, Maeno T, Iki M, Kuniyoshi M. 1964. Reciprocal activities of the ventromedial and lateral hypothalamic area of cats. Science 143:484–485 - PubMed
-
- Oomura Y, Nakamura T, Sugimori M, Yamada Y. 1975. Effect of free fatty acid on the rat lateral hypothalamic neurons. Physiol Behav 14:483–486 - PubMed
-
- Levin BE, Routh VH, Kang L, Sanders NM, Dunn-Meynell AA. 2004. Neuronal glucosensing: what do we know after 50 years? Diabetes 53:2521–2528 - PubMed

