Liver enzymes are associated with hepatic insulin resistance, insulin secretion, and glucagon concentration in healthy men and women
- PMID: 21521874
- PMCID: PMC3114399
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1806
Liver enzymes are associated with hepatic insulin resistance, insulin secretion, and glucagon concentration in healthy men and women
Abstract
Objective: The pathophysiological mechanisms to explain the association between risk of type 2 diabetes and elevated concentrations of γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT) and alanineaminotransferase (ALT) remain poorly characterized. We explored the association of liver enzymes with peripheral and hepatic insulin resistance, insulin secretion, insulin clearance, and glucagon concentration.
Research design and methods: We studied 1,309 nondiabetic individuals from the Relationship between Insulin Sensitivity and Cardiovascular disease (RISC) study; all had a euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp and an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with assessment of insulin secretion and hepatic insulin extraction. The hepatic insulin resistance index was calculated in 393 individuals.
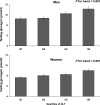
Results: In both men and women, plasma concentrations of GGT and ALT were inversely related with insulin sensitivity (M/I) (all P < 0.01). Likewise, the hepatic insulin resistance index was positively correlated with both GGT (r = 0.37, P < 0.0001, men; r = 0.36, P < 0.0001, women) and ALT (r = 0.25, P = 0.0005, men; r = 0.18, P = 0.01, women). These associations persisted in multivariable models. Increased GGT and ALT were significantly associated with higher insulin secretion rates and with both reduced endogenous clearance of insulin and hepatic insulin extraction during the OGTT (P = 0.0005 in men; P = 0.003 in women). Plasma fasting glucagon levels increased over ALT quartiles (men, quartile 4 vs. quartile 1 11.2 ± 5.1 vs. 9.3 ± 3.8 pmol/L, respectively, P = 0.0002; women, 9.0 ± 4.3 vs. 7.6 ± 3.1, P = 0.001).
Conclusions: In healthy individuals, increased GGT and ALT were biomarkers of both systemic and hepatic insulin resistance with concomitant increased insulin secretion and decreased hepatic insulin clearance. The novel finding of a positive correlation between ALT and fasting glucagon level concentrations warrants confirmation in type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Comment in
-
Potential mechanisms underlying the associations between liver enzymes and risk for type 2 diabetes.Hepatology. 2012 Mar;55(3):968-70. doi: 10.1002/hep.24769. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22362600 No abstract available.
References
-
- André P, Balkau B, Vol S, Charles MA, Eschwège E; DESIR Study Group Gamma-glutamyltransferase activity and development of the metabolic syndrome (International Diabetes Federation Definition) in middle-aged men and women: data from the Epidemiological Study on the Insulin Resistance Syndrome (DESIR) cohort. Diabetes Care 2007;30:2355–2361 - PubMed
-
- Perry IJ, Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG. Prospective study of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1998;21:732–737 - PubMed
-
- Lee DH, Silventoinen K, Jacobs DR, Jr, Jousilahti P, Tuomileto J. gamma-Glutamyltransferase, obesity, and the risk of type 2 diabetes: observational cohort study among 20,158 middle-aged men and women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:5410–5414 - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi N, Suzuki K, Tatara K. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Japanese men. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1427–1432 - PubMed
-
- Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Lennon L, Whincup PH. Hepatic enzymes, the metabolic syndrome, and the risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2913–2918 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

