Prevalence of and risk factors for lipodystrophy among HIV-infected patients receiving combined antiretroviral treatment in the Asia-Pacific region: results from the TREAT Asia HIV Observational Database (TAHOD)
- PMID: 21521929
- PMCID: PMC3329967
- DOI: 10.1507/endocrj.k10e-407
Prevalence of and risk factors for lipodystrophy among HIV-infected patients receiving combined antiretroviral treatment in the Asia-Pacific region: results from the TREAT Asia HIV Observational Database (TAHOD)
Abstract
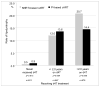
The prevalence of and risk factors for lipodystrophy (LD) among patients receiving combined antiretroviral treatment (cART) in the Asia-Pacific region are largely unknown. LD diagnosis was based on the adverse event definition from the US NIH Division of AIDS (2004 version), and only cases with a severity grade of ≥ 3 were included. TAHOD patients who had recently commenced cART with ≥ 3 drugs after 1996 from sites which had ever reported LD were included in the analysis. Covariates for the forward multivariate logistic regression model included demographic variables, CDC disease classification, baseline CD4 and viral load, hepatitis B/C virus co-infection, and regimen and duration of cART. LD was diagnosed in 217 (10.5%) of 2072 patients. The median duration of cART was 3.8 (interquartile range, 2.2-5.3) years [stavudine, 2.0 (1.0-3.5) years; zidovudine, 1.8 (0.6-3.9) years; and protease inhibitors (PI), 2.6 (1.3-4.5) years]. In the multivariate model, factors independently associated with LD included use of stavudine (≤ 2 years vs. no experience: OR 25.46, p<0.001, > 2 years vs. no experience: OR 14.92, p<0.001), use of PI (> 2.6 years vs. no experience: OR 0.26, p<0.001), and total duration of cART (> vs. ≤ 3.8 years: OR 4.84, p<0.001). The use of stavudine was strongly associated with LD in our cohort. Stavudine-sparing cART strategies are warranted to prevent the occurrence of LD in the Asia-Pacific region.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Carr A, Cooper DA. Images in clinical medicine. Lipodystrophy associated with an HIV-protease inhibitor. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1296. - PubMed
-
- Grinspoon S, Carr A. Cardiovascular risk and body-fat abnormalities in HIV-infected adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:48–62. - PubMed
-
- Spire B, Carrieri P, Sopha P, Protopopescu C, Prak N, Quillet C, Ngeth C, Ferradini L, Delfraissy JF, Laureillard D. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy in patients enrolled in a comprehensive care program in Cambodia: a 24-month follow-up assessment. Antivir Ther. 2008;13:697–703. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes AP, Sanches RS, Mill J, Lucy D, Palha PF, Dalri MC. Lipodystrophy syndrome associated with antiretroviral therapy in HIV patients: considerations for psychosocial aspects. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2007;15:1041–1045. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Paton NI, Ditangco R, Chen YM, Kamarulzaman A, Kumarasamy N, Lee CK, Li PC, Merati TP, Phanuphak P, Pujari S, Vibhagool A, Zhang F, Chuah J, Frost KR, Cooper DA, Law MG. Experience with the use of a first-line regimen of stavudine, lamivudine and nevirapine in patients in the TREAT Asia HIV Observational Database. HIV Med. 2007;8:8–16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

