Microfluidic enrichment of small proteins from complex biological mixture on nanoporous silica chip
- PMID: 21522500
- PMCID: PMC3082347
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3528237
Microfluidic enrichment of small proteins from complex biological mixture on nanoporous silica chip
Abstract
The growing field of miniaturized diagnostics is hindered by a lack of pre-analysis treatments that are capable of processing small sample volumes for the detection of low concentration analytes in a high-throughput manner. This letter presents a novel, highly efficient method for the extraction of low-molecular weight (LMW) proteins from biological fluids, represented by a mixture of standard proteins, using integrated microfluidic systems. We bound a polydimethylsiloxane layer patterned with a microfluidic channel onto a well-defined nanoporous silica substrate. Using rapid, pressure-driven fractionation steps, this system utilizes the size-exclusion properties of the silica nanopores to remove high molecular weight proteins while simultaneously isolating and enriching LMW proteins present in the biological sample. The introduction of the microfluidic component offers important advantages such as high reproducibility, a simple user interface, controlled environment, the ability to process small sample volumes, and precise quantification. This solution streamlines high-throughput proteomics research on many fronts and may find broad acceptance and application in clinical diagnostics and point of care detection.
Figures

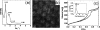

References
-
- Hye A., Lynham S., Thambisetty M., Causevic M., Campbell J., Byers H. L., Hooper C., Rijsdijk F., Tabrizi S. J., Banner S., Shaw C. E., Foy C., Poppe M., Archer N., Hamilton G., Powell J., Brown R. G., Sham P., Ward M., and Lovestone S., Brain BRAIAK 129, 3042 (2006).10.1093/brain/awl279 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
