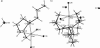fac-{2-[Bis(2-amino-eth-yl)amino]-ethanaminium}trichloridorhodium(III) chloride hemihydrate
- PMID: 21522607
- PMCID: PMC3050386
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810051846
fac-{2-[Bis(2-amino-eth-yl)amino]-ethanaminium}trichloridorhodium(III) chloride hemihydrate
Abstract
The crystal structure of the title compound, [Rh(C(6)H(19)N(4))Cl(3)]Cl·0.5H(2)O, is isotypic with the previously reported Ru analogue. The structure contains two crystallographically independent [Rh(Htren)Cl(3)](+) cations with a facial tridentate coordination of the monoprotonated tren ligand [tren = tris-(2-amino-eth-yl)amine], leading to an overall distorted octahedral coordination environment around the Rh(III) atom. In one of the two cations, the ethyl-ene groups of the two chelate rings as well as the non-coordinating ethyl-ammonium group are disordered over two sets of sites [0.579 (3):0.421 (3) occupancy ratio]. A series of N-H⋯Cl and O-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds stabilizes the structure.
Figures
References
-
- Blackman, A. G. (2005). C. R. Chim. 8, 107–119.
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2010). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Bruker (2010). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Düpre, Y., Bartscherer, E., Sander, J., Huch, V. & Hegetschweiler, K. (1999). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 214, 407–409.
-
- Hirshfeld, F. L. (1976). Acta Cryst. A32, 239–244.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous