Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and macroautophagy in inflammation and infection
- PMID: 21524386
- PMCID: PMC3285235
Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and macroautophagy in inflammation and infection
Abstract
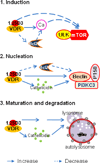
Vitamin D is involved in mineral and bone homeostasis, immune responses, anti-inflammation, anti-infection, and cancer prevention. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) is a nuclear receptor that mediates most biological functions of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) or vitamin D(3), the active form of vitamin D. Recently, vitamin D(3)-induced autophagy has been reported. Autophagy is a lysosome-mediated catabolic pathway classified into three different types: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy. Autophagy contributes to anti-aging, antimicrobial defense, and tumor suppression. The functions of autophagy overlap remarkably with those of vitamin D/VDR signaling. This review focuses on vitamin D(3), VDR, and macroautophagy in inflammation and infection. We place emphasis on the regulatory roles of vitamin D(3) on autophagy at different steps, including induction, nucleation, elongation to maturation, and degradation. We summarize the known molecular mechanisms of vitamin D/VDR signaling on autophagy homeostasis. The potential application of the insights gleaned from these research findings to anti-inflammation and anti-infection is also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adams JS, Chen H, Chun R, Gacad MA, Encinas C, Ren S, Nguyen L, Wu S, Hewison M, Barsony J. Response element binding proteins and intracellular vitamin D binding proteins: novel regulators of vitamin D trafficking, action and metabolism. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;89–90(1–5):461–465. - PubMed
-
- Adisen E, Gulekon A, Erdem O, Dursun A, Gurer MA. The effects of calcipotriol and methylprednisolone aseponate on bcl-2, p53 and ki-67 expression in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20(5):527–533. - PubMed
-
- Adorini L, Penna G. Control of autoimmune diseases by the vitamin D endocrine system. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4(8):404–412. - PubMed
-
- Albert PJ, Proal AD, Marshall TG. Vitamin D: the alternative hypothesis. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8(8):639–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

