Programmed death 1 regulates development of central memory CD8 T cells after acute viral infection
- PMID: 21525385
- PMCID: PMC3854944
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003870
Programmed death 1 regulates development of central memory CD8 T cells after acute viral infection
Abstract
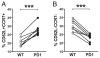
The T cell response possesses a number of inhibitory receptors to regulate the extent of the antiviral response and prevent immune pathology. These receptors are generally transiently upregulated during an effector response and then downregulated during memory. Some inhibitory receptors, such as programmed death 1 (PD-1) and LAG-3, were shown to be aberrantly upregulated during memory to chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, limiting functional capabilities. However, little is known about the impact of inhibitory receptors on memory development during a normal CD8 T cell response to acute virus infection. Our previous data showed that PD-1 is aberrantly upregulated during a secondary response by memory CD8 T cells that were generated without CD4 T cell help. Therefore, we examined the role of PD-1 in memory differentiation during acute vaccinia virus infection in intact mice. In the absence of PD-1, the primary and memory CD8 T cell responses were enhanced. Moreover, there were distinct phenotypic and functional changes in the memory PD-1(-/-) CD8 T cells. Higher levels of CD62L, CD27, and CCR7 were detected; cells produced more IL-2 and made an enhanced secondary response. These changes indicate a skewing of the memory population toward the central memory phenotype in the absence of PD-1 signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Shin H, Wherry EJ. CD8 T cell dysfunction during chronic viral infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:408–415. - PubMed
-
- Vibhakar R, Juan G, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z, Finger LR. Activation-induced expression of human programmed death-1 gene in T-lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1997;232:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Scheipers P, Reiser H. Role of the CTLA-4 receptor in T cell activation and immunity. Physiologic function of the CTLA-4 receptor. Immunol Res. 1998;18:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Workman CJ, Cauley LS, Kim IJ, Blackman MA, Woodland DL, Vignali DA. Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (CD223) regulates the size of the expanding T cell population following antigen activation in vivo. J Immunol. 2004;172:5450–5455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

