Mechanisms of protein retention in the Golgi
- PMID: 21525512
- PMCID: PMC3140682
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005264
Mechanisms of protein retention in the Golgi
Abstract
The protein composition of the Golgi is intimately linked to its structure and function. As the Golgi serves as the major protein-sorting hub for the secretory pathway, it faces the unique challenge of maintaining its protein composition in the face of constant influx and efflux of transient cargo proteins. Much of our understanding of how proteins are retained in the Golgi has come from studies on glycosylation enzymes, largely because of the compartment-specific distributions these proteins display. From these and other studies of Golgi membrane proteins, we now understand that a variety of retention mechanisms are employed, the majority of which involve the dynamic process of iterative rounds of retrograde and anterograde transport. Such mechanisms rely on protein conformation and amino acid-based sorting signals as well as on properties of transmembrane domains and their relationship with the unique lipid composition of the Golgi.
Figures
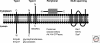
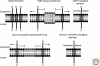
References
-
- Abe M, Noda Y, Adachi H, Yoda K 2004. Localization of GDP-mannose transporter in the golgi requires retrieval to the endoplasmic reticulum depending on its cytoplasmic tail and coatomer. J Cell Sci 117: 5687–5696 - PubMed
-
- Ballensiefen W, Ossipov D, Schmitt HD 1998. Recycling of the yeast v-SNARE Sec22p involves COPI-proteins and the ER transmembrane proteins Ufe1p and Sec20p. J Cell Sci 111 (Pt 11): 1507–1520 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
