Use of fondaparinux in a pregnant woman with pulmonary embolism and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 21525816
- PMCID: PMC3539579
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.881753
Use of fondaparinux in a pregnant woman with pulmonary embolism and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Abstract
Background: A serious complication of heparin treatment, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is rarely observed in pregnant women. Drug therapy during pregnancy should always be chosen to minimize fetal risk. The management of HIT in pregnancy represents a medical challenge. Unlike heparins, the anticoagulants used in patients with HIT do cross the placenta, with unknown fetal effects.
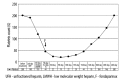
Case report: We present a case of a 24-year-old female presenting for care at 34 weeks of gestation with acute pulmonary embolism treated initially with unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), who developed HIT. She was then successfully treated with fondaparinux.
Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first case reports describing a successful use of fondaparinux in the treatment of HIT in a third-trimester pregnant woman, providing a novel approach for this subset of patients.
Figures
References
-
- Heit JA, Kobbervig CE, James AH, et al. Trends in the incidence of venous thromboembolism during pregnancy or postpartum: a 30-year population based study. Ann Intern Med. 2005;36:697–706. - PubMed
-
- Rutherford SE, Phelan JP. Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1991;18:345–70. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan EA, Ford JB, Chambers G, Slaytor EK. Maternal mortality in Australia, 1973–1996. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;44:452–57. - PubMed
-
- Bates SM, Greer IA, Pabinger I, et al. Venous thromboembolism, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy. Chest. 2008;133(Suppl 6):844S–886S. - PubMed
-
- Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2276–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical