Early postoperative serum cystatin C predicts severe acute kidney injury following pediatric cardiac surgery
- PMID: 21525851
- PMCID: PMC3312809
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.123
Early postoperative serum cystatin C predicts severe acute kidney injury following pediatric cardiac surgery
Abstract
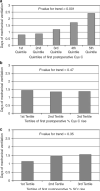
In this multicenter, prospective study of 288 children (half under 2 years of age) undergoing cardiac surgery, we evaluated whether the measurement of pre- and postoperative serum cystatin C (CysC) improves the prediction of acute kidney injury (AKI) over that obtained by serum creatinine (SCr). Higher preoperative SCr-based estimated glomerular filtration rates predicted higher risk of the postoperative primary outcomes of stage 1 and 2 AKI (adjusted odds ratios (ORs) 1.5 and 1.9, respectively). Preoperative CysC was not associated with AKI. The highest quintile of postoperative (within 6 h) CysC predicted stage 1 and 2 AKI (adjusted ORs of 6 and 17.2, respectively). The highest tertile of percent change in CysC independently predicted AKI, whereas the highest tertile of SCr predicted stage 1 but not stage 2 AKI. Postoperative CysC levels independently predicted longer duration of ventilation and intensive care unit length of stay, whereas the postoperative SCr change only predicted longer intensive care unit stay. Thus, postoperative serum CysC is useful to risk-stratify patients for AKI treatment trials. More research, however, is needed to understand the relation between preoperative renal function and the risk of AKI.
Figures

Comment in
-
The challenges of assessing acute kidney injury in infants.Kidney Int. 2011 Sep;80(6):567-8. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.172. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 21878953
References
-
- D'Onofrio A, Cruz D, Bolgan I, et al. RIFLE criteria for cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: risk factors and outcomes. Congest Heart Fail. 2010;16(Suppl 1):S32–S36. - PubMed
-
- Li SY, Chen JY, Yang WC, et al. Acute kidney injury network classification predicts in-hospital and long-term mortality in patients undergoing elective coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;39:323–328. - PubMed
-
- Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, et al. A small postoperative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int. 2009;76:885–892. - PubMed
-
- Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, et al. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:1012–1024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

