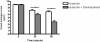A comparison of the effect of intranasal desmopressin and intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide combination with intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide alone in acute renal colic
- PMID: 21526084
- PMCID: PMC3082813
A comparison of the effect of intranasal desmopressin and intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide combination with intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide alone in acute renal colic
Abstract
Background: Patients with acute renal colic usually require immediate diagnosis and treatment. In this clinical trial analgesic effect of hyoscine N-butyl bromide and desmopressin combination in comparison with hyoscine N-butyl bromide alone in patients with acute renal colic induced by urinary stones was assessed.
Methods: The study included 114 patients randomly allocated in two groups (A and B). Patients in group A received 20 mg intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide at admission time and patients in group B received 20 μg of intranasal desmopressin in combination with 20 mg intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide. A visual analogue scale (VAS; a 10-cm horizontal scale ranging from "zero or no pain" to "10 or unbearable pain") was hired to assess the patients' pain severity at baseline, 30 and 60 minutes after the treatments.
Results: ON ADMISSION, THE PAIN LEVEL WAS SIMILAR IN BOTH GROUPS (GROUP A: 8.95 ± 0.11 and group B: 8.95 ± 0.12). In group A, the mean of pain level showed a decrease after 30 minutes (group A: 7.26 ± 0.25 and group B: 5.95 ± 0.28) but further decreasing did not occur; however in group B, the pain consistently decreased and the mean after 60 minutes was significantly decreased (group A: 6.80 ± 0.31 and group B: 3.71 ± 0.31). No side effects were detected in this study.
Conclusions: The combination of hyoscine N-butyl bromide and desmopressin is more effective than hyoscine N-butyl bromide alone in patients with renal colic. Further studies are recommended to validate these findings and compare the different doses of desmopressin.
Keywords: Analgesia; Calculus; Desmopressin; Renal Colic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Leslie SW. Nephrolithiasis, acute renal colic. 2006. Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/456872-overview Accessed March 3.
-
- Curhan GC, Aronson MD, Preminger GM. Diagnosis and acute management of suspected nephrolithiasis in adults. 2009. Available from: http://www.uptodate.com/patients/content/topic.do?topicKey=~PEEs8wkDGf.a... Accessed October 5.
-
- el-Sherif AE, Salem M, Yahia H, al-Sharkawy WA, al-Sayrafi M. Treatment of renal colic by desmopressin intranasal spray and diclofenac sodium. J Urol. 1995;153(5):1395–8. - PubMed
-
- Al-Faddagh ZA, Jawad AM, Salman JM. Comparative placebo-controlled study on the efficacy of hyoscine-N-butylbromide and diclofenac sodium in treatment of clinically diagnosed renal colic. Basrah J Surg. 1996;2(1):16–20.
-
- Holdgate A, Oh CM. Is there a role for antimuscarinics in renal colic.A randomized controlled trial? J Urol. 2005;174(2):572–5. discussion 575. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous