A user's guide to the encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE)
- PMID: 21526222
- PMCID: PMC3079585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001046
A user's guide to the encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE)
Abstract
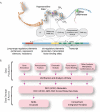
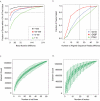
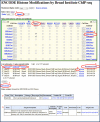
The mission of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Project is to enable the scientific and medical communities to interpret the human genome sequence and apply it to understand human biology and improve health. The ENCODE Consortium is integrating multiple technologies and approaches in a collective effort to discover and define the functional elements encoded in the human genome, including genes, transcripts, and transcriptional regulatory regions, together with their attendant chromatin states and DNA methylation patterns. In the process, standards to ensure high-quality data have been implemented, and novel algorithms have been developed to facilitate analysis. Data and derived results are made available through a freely accessible database. Here we provide an overview of the project and the resources it is generating and illustrate the application of ENCODE data to interpret the human genome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

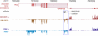


References
-
- Collins F. S, Green E. D, Guttmacher A. E, Guyer M. S. A vision for the future of genomics research. Nature. 2003;422:835–847. - PubMed
-
- ENCODE Project Consortium. The ENCODE (ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements) Project. Science. 2004;306:636–640. - PubMed
-
- Mouse Genome Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520–562. - PubMed
-
- Chiaromonte F, Weber R. J, Roskin K. M, Diekhans M, Kent W. J, Haussler D. The share of human genomic DNA under selection estimated from human-mouse genomic alignments. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2003;68:245–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

