Structural basis for methyl transfer by a radical SAM enzyme
- PMID: 21527678
- PMCID: PMC3506250
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1205358
Structural basis for methyl transfer by a radical SAM enzyme
Abstract
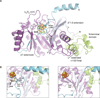
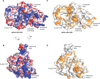
The radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) enzymes RlmN and Cfr methylate 23S ribosomal RNA, modifying the C2 or C8 position of adenosine 2503. The methyl groups are installed by a two-step sequence involving initial methylation of a conserved Cys residue (RlmN Cys(355)) by SAM. Methyl transfer to the substrate requires reductive cleavage of a second equivalent of SAM. Crystal structures of RlmN and RlmN with SAM show that a single molecule of SAM coordinates the [4Fe-4S] cluster. Residue Cys(355) is S-methylated and located proximal to the SAM methyl group, suggesting the SAM that is involved in the initial methyl transfer binds at the same site. Thus, RlmN accomplishes its complex reaction with structural economy, harnessing the two most important reactivities of SAM within a single site.
Figures
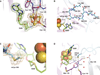
References
-
- Markham GD. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2010.
-
- Woodard RW, Tsai MD, Floss HG, Crooks PA, Coward JK. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:9124. - PubMed
-
- Hegazi MF, Borchardt RT, Schowen RL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979;101:4359.
-
- Frey PA, Hegeman AD. Enzymatic Reaction Mechanisms. Oxford University Press; New York: 2007.
-
- Iwig DF, Grippe AT, McIntyre TA, Booker SJ. Biochemistry. 2004;43:13510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

