Triglycerides and heart disease: still a hypothesis?
- PMID: 21527746
- PMCID: PMC3141088
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.226100
Triglycerides and heart disease: still a hypothesis?
Abstract
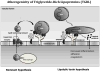
The purpose of this article is to review the basic and clinical science relating plasma triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Although many aspects of the basic physiology of triglyceride production, its plasma transport, and its tissue uptake have been known for several decades, the relationship of plasma triglyceride levels to vascular disease is uncertain. Are triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, their influence on high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein, or the underlying diseases that lead to defects in triglyceride metabolism the culprit? Animal models have failed to confirm that anything other than early fatty lesions can be produced by triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Metabolic products of triglyceride metabolism can be toxic to arterial cells; however, these studies are primarily in vitro. Correlative studies of fasting and postprandial triglycerides and genetic diseases implicate very-low-density lipoprotein and their remnants and chylomicron remnants in atherosclerosis development, but the concomitant alterations in other lipoproteins and other risk factors obscure any conclusions about direct relationships between disease and triglycerides. Genes that regulate triglyceride levels also correlate with vascular disease. Human intervention trials, however, have lacked an appropriately defined population and have produced outcomes without definitive conclusions. The time is more than ripe for new and creative approaches to understanding the relationship of triglycerides and heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure - The authors have no relationships that could be perceived as real or apparent conflict(s) of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Voyiaziakis E, Goldberg IJ, Plump AS, Rubin EM, Breslow JL, Huang LS. ApoA-I deficiency causes both hypertriglyceridemia and increased atherosclerosis in human apoB transgenic mice. J Lipid Res. 1998;39:313–321. - PubMed
-
- Chung S, Timmins JM, Duong M, Degirolamo C, Rong S, Sawyer JK, Singaraja RR, Hayden MR, Maeda N, Rudel LL, Shelness GS, Parks JS. Targeted deletion of hepatocyte ABCA1 leads to very low density lipoprotein triglyceride overproduction and low density lipoprotein hypercatabolism. J Biol Chem. 285:12197–12209. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Willnow TE, Sheng Z, Ishibashi S, Herz J. Inhibition of hepatic chylomicron remnant uptake by gene transfer of a receptor antagonist. Science. 1994;264:1471–1474. - PubMed
-
- Out R, Kruijt JK, Rensen PC, Hildebrand RB, de Vos P, Van Eck M, Van Berkel TJ. Scavenger receptor BI plays a role in facilitating chylomicron metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18401–18406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

